Google Ranking Factors: A Complete List of 200 Known Factors
A lot of SEO beginners think that good content enriched with keywords and backlinks is all they need to rank on the first page of Google’s search results.
While they are not entirely wrong, there are a lot of other Google ranking factors that can affect their search rankings.
Did you know that Google uses over 200 different ranking factors to rank its search results?
At least, these 200 ranking factors are the ones we know of and Google may be using a lot more. You will need a working knowledge of all these Google ranking factors if you want to succeed in your SEO journey.
In this post, we will discuss:
- What exactly are Google ranking factors (categorization)
- The top Google ranking factors and how to optimize for them
- A complete list of the 200 known Google ranking factors
So, let’s get started.

What are the Google Ranking Factors?
Google ranking factors are signals, metrics, and other factors that Google uses to prioritize and rank search results for each search query.
These ranking factors can be categorized under the following categories:
- Domain ranking factors
- Page-level ranking factors
- Backlink ranking factors
- User interaction factors
- Special Google algorithm rules
- Brand signals
- On-Site webspam factors
- Off-Site webspam factors

Which are the Top Ten Google Ranking Factors?
In this section, we will discuss the top Google ranking factors that you should focus on in your SEO journey. If you optimize these right, you will see a marked improvement in your SEO performance.
However, if you want the complete list of 200 Google ranking factors, you can skip to the next section.
1. Content Quality
Everyone knows that good content is one of the top Google ranking factors.
But, do you know what Google considers as good content?
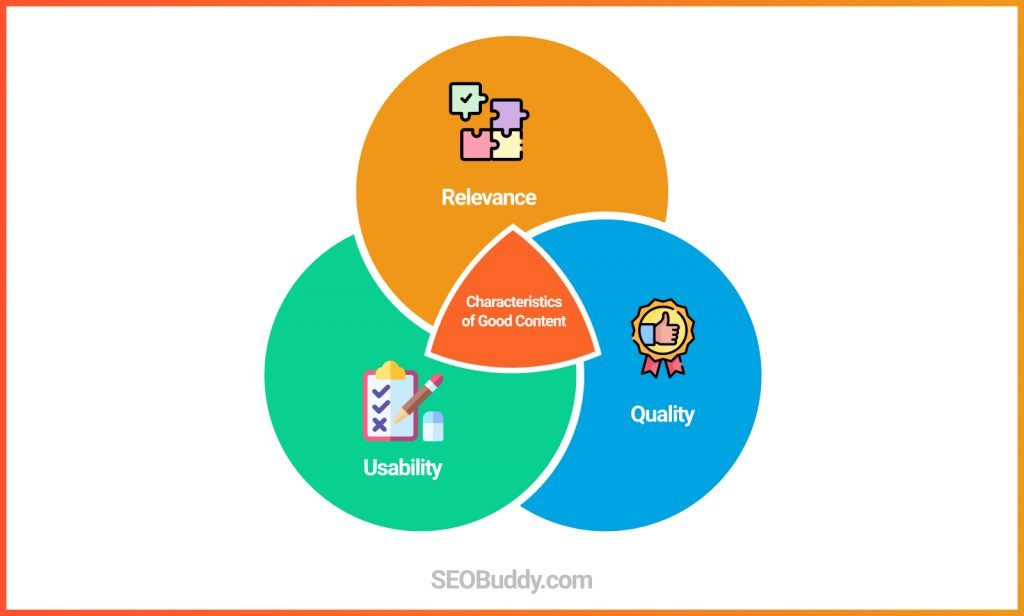
There are 3 main aspects:
Relevance – Whether or not your content answers the user’s question or provides the information they are looking for.
Quality – How well or in-depth does the content cover the topic at hand and how does it compare to the other content on the same topic.
Usability – Whether the content is practically easy to understand and use by the readers and can be accessed on all types of devices.
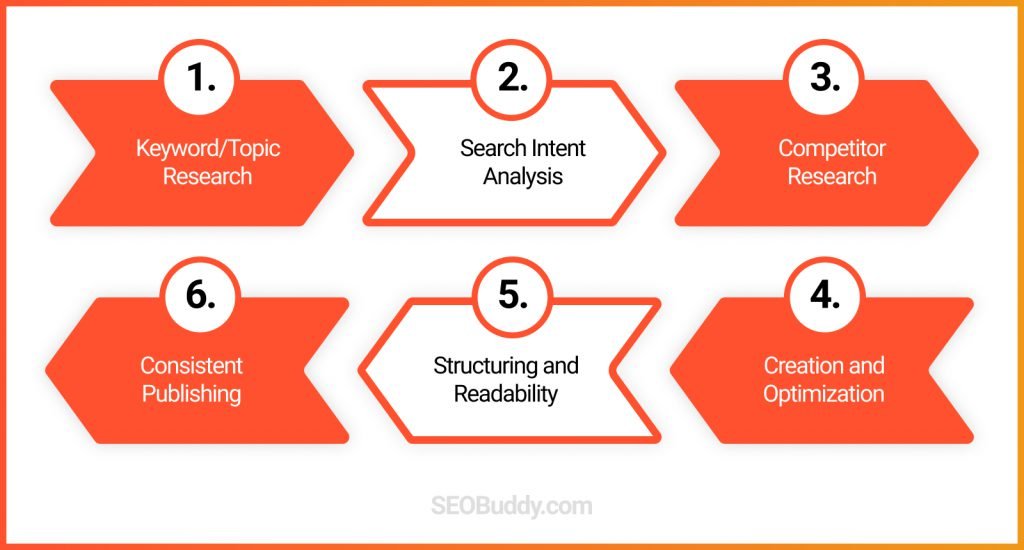
How can you create content that ranks?
Here are some tips:
- Choose your keywords and topics carefully, after conducting thorough keyword research.
- Check the user intent and see what kind of content shows up when you type a keyword.
- Go through the other content on the topic and create better and more in-depth content.
- Optimize your content with different types of keywords including primary and LSI keywords.
- Make sure that your content is structured well into different sections and is easy to read and understand.
- Publish high-quality, relevant content frequently and consistently to improve your website’s authority.
2. Keyword Optimization
Keyword optimization is probably the second-most important on-page SEO ranking factor after content.
Today, we will discuss two key aspects of keyword optimization—keyword placement and keyword density.
So, let’s get started.
Keyword Placement
For every piece of content that you create, you need to have one primary or target keyword and a few LSI keywords.
To rank higher on Google search results, you should place your keywords (at least primary keyword) in:
- Meta descriptions
- Title tags
- H1 tags
- H2 and H3 tags
- First 100 words of content
- Throughout the content
- URL
- Image alt text, name, and description
Keyword Density
While the placement of keywords at strategic locations holds a lot of weight, it is also important to maintain the right keyword density throughout the content.
If you over-optimize, then Google will consider your content spammy and if you under-optimize your rankings might get affected.
So, what’s the sweet spot?
As a general rule, maintain a density of 1% to 1.5% for articles and over 2% for landing pages.

3. Organic Click-Through-Rate
One of the most important Google ranking factors that few people talk about is organic CTR.
The more people click on your page in search results, the more Google will consider your content as relevant for a particular search query.
This is where your title tag and meta descriptions play an important role. These are the first things anyone sees when deciding whether to read your content or not.
You need to write catchy and relevant titles and meta descriptions to increase your organic CTR.
How?
Here are a few tips:
- Clearly describe your content and what readers will gain from it.
- Use action words that encourage people to click on it and read.
- Place your target keyword right at the beginning of meta descriptions.
- Use stats, numbers, and power words in your titles.
Also, keep these short and crisp.
- 50-60 characters is the ideal length for title tags
- 150-160 characters is ideal for meta descriptions

4. Authoritativeness and Expertise
Even if you produce high-quality content, optimized with keywords, you may still rank low if your domain authority is low. Similarly, Google may rank your content higher for niche queries if it considers your site as an expert in that niche.
Domain authority, in and of itself, is not one of the Google ranking factors as it is a score created by Moz. However, the signals that Moz uses to determine a website’s domain authority are more or less similar to the Google ranking factors that determine authority.
Google uses several different ranking factors and trust signals to determine the authoritativeness and expertise of a website. Some of these factors include:
- Number and quality of backlinks
- Quality of referring domains
- Current keyword rankings
You need to improve your overall SEO performance, especially strengthen your backlink profile, to increase your authority. The best way to do that is to use a detailed SEO checklist that covers all aspects of SEO. Luckily for you, we have already created an ultimate SEO checklist that you can simply download and start using.
Expertise, on the other hand, is determined by the quality of your content and the frequency of posting high-quality content.
You can show your expertise in your niche by creating topic clusters and covering all important keywords in extreme detail. Create multiple content pieces on related keywords that revolve around a central keyword or theme.
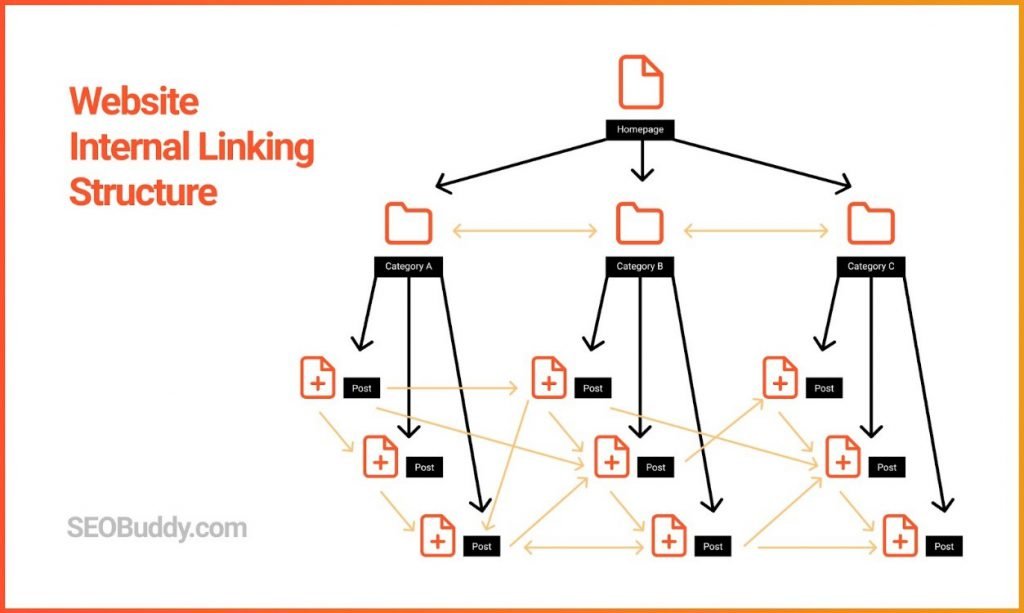
Internal linking also helps with rankings and the more internal linking you will have among multiple pages with related keywords, the better. This shows that you have expertise on a particular topic and you will have higher chances of ranking for it.
5. Mobile-Friendliness
After Google’s mobile-friendly update, mobile responsiveness has joined the list of top Google ranking factors.
All things remaining the same, Google prefers to rank sites that can be easily accessed from all kinds of devices. Mobile-friendly sites are rewarded with higher rankings and sites that don’t render well on mobile devices are punished.
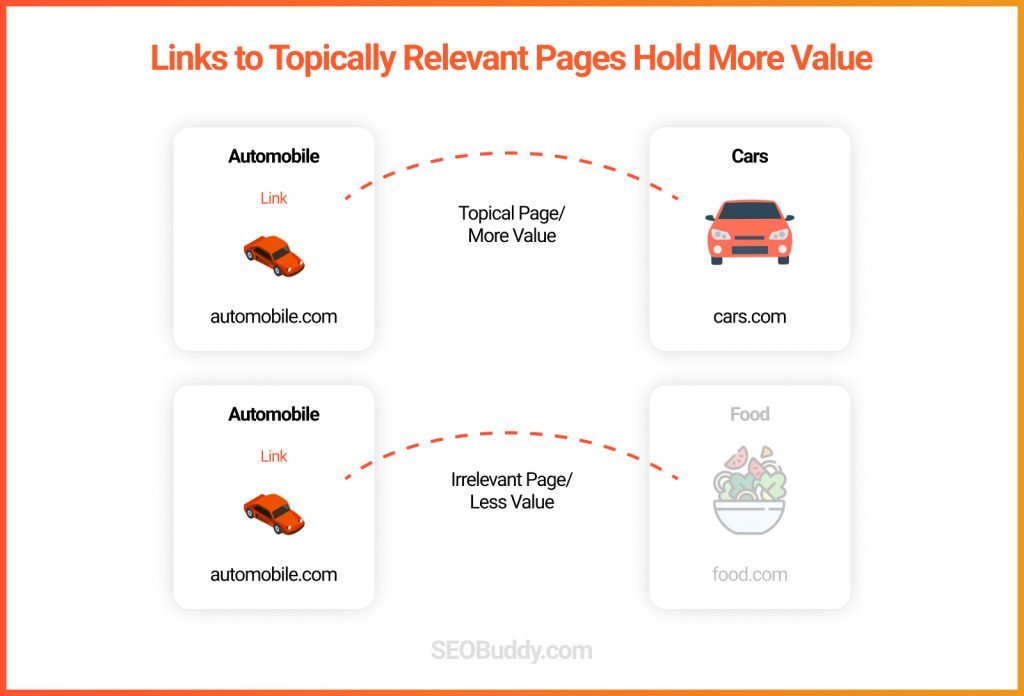
Want to know whether your website is mobile-friendly or not?
Check it using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
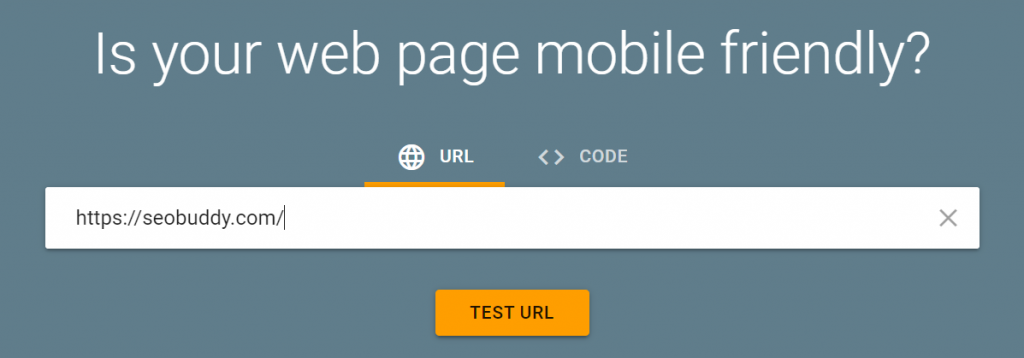
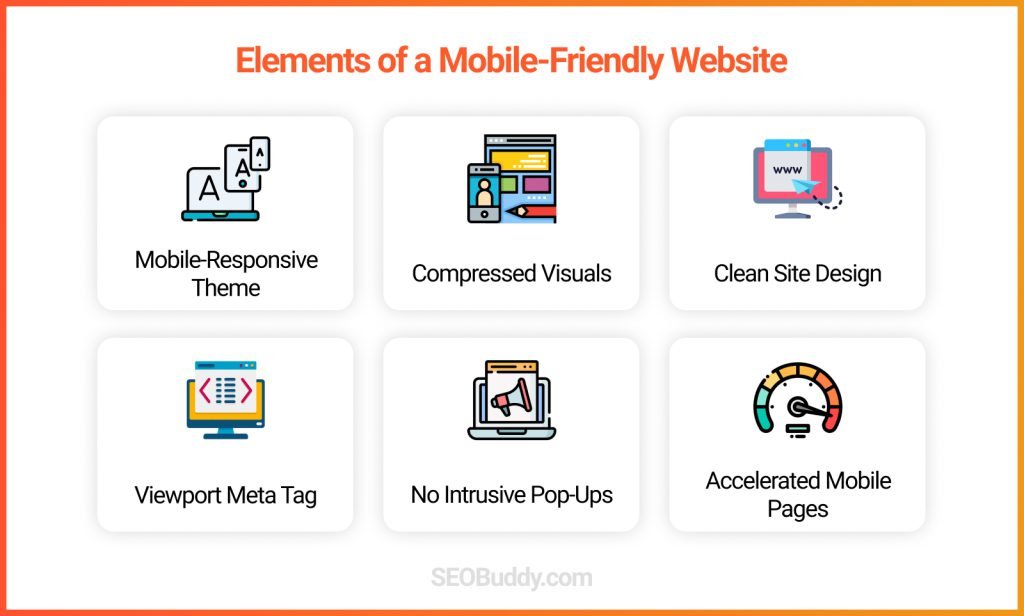
If it is not, then you need to take the following steps to make it mobile-friendly:
- Use a mobile-responsive theme for your website
- Compress the file sizes of your on-page visuals
- Use a clean and simple website layout and design
- Add the viewport meta tag to your site’s HTML code

- Avoid using pop-up ads or forms that block your content
- Use Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) to improve mobile responsiveness
6. Backlink Profile
Content, keywords, and authority were all Google ranking factors related to on-page SEO. When it comes to off-page SEO ranking factors, however, nothing holds more weight than a strong backlink profile.
Let us clarify, though, that a strong backlink profile is a combination of several Google ranking factors like:
- Number of backlinks
- Number of referring domains
- Quality of referring domains
- Quality of backlinks
- And more!
However, for the sake of simplicity, let’s cover it as a whole, because that’s what Google does when ranking various pages.
So, how can you strengthen your backlink profile?
For that, you need to build more high-quality backlinks to your website.
Here are some link-building tactics that you can use:
- Contribute guest posts on authoritative websites
- Create and distribute infographics with links in the description
- Reclaim broken links by providing correct or updated links
- Ask for backlinks from all unlinked brand mentions
- Participate in expert roundups and interviews
- Join relevant Quora forums and add links in answers
- Provide HARO answers with relevant backlinks to your site
- Claim your GMB and local directory listings and add links to each

Here are some link-building best practices to ensure a high-quality backlink profile:
- Always use a relevant anchor text that clearly shows where a user will be directed if they click on the link.
- Don’t use the same anchor text multiple times, but use variations to maintain a natural and diverse backlink profile.
- Make sure that you get backlinks from recent or regularly updated pages and remove backlinks from old and outdated pages.
- Focus more on getting backlinks from authoritative sites than low-authority sites, as the former holds more weight.
- Place backlinks within the main content and don’t hide them in sidebars, headers, footers, etc.
- Always add backlinks to relevant content that is related to the topic at hand.
- Don’t link to bad link neighborhoods like spammy sites, gambling or illegal sites, link farms, etc.
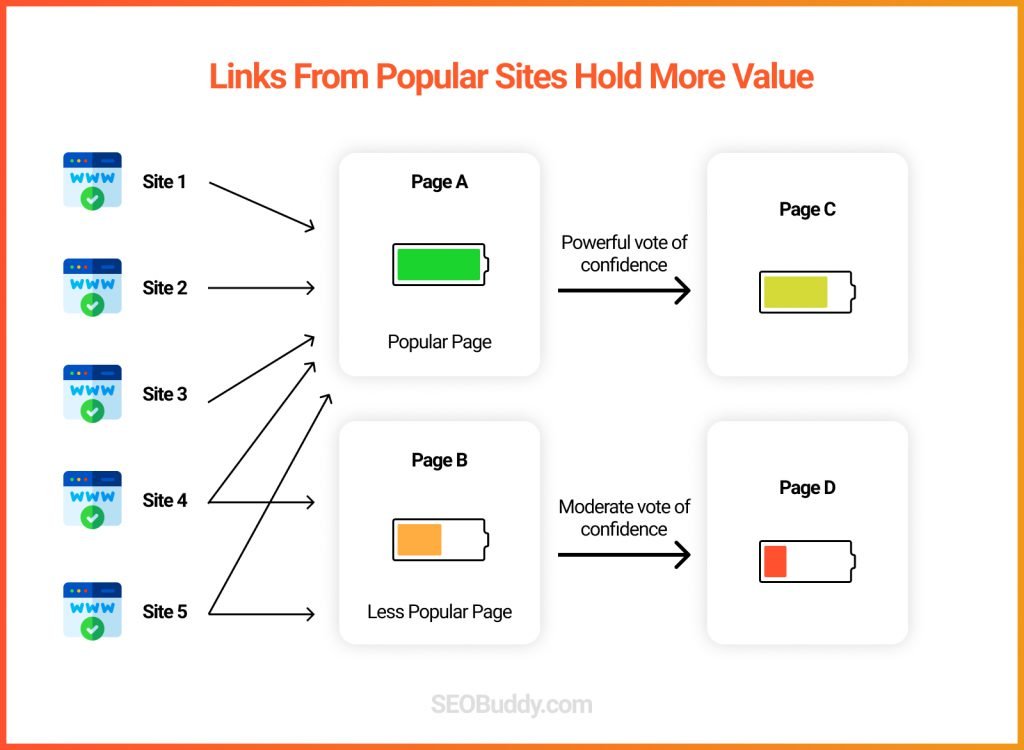
- Get backlinks from popular pages to get some of that PageRank juice and vote of confidence.

7. Structured Data
This is another one of the top Google ranking factors because it directly helps you rank higher on SERP.
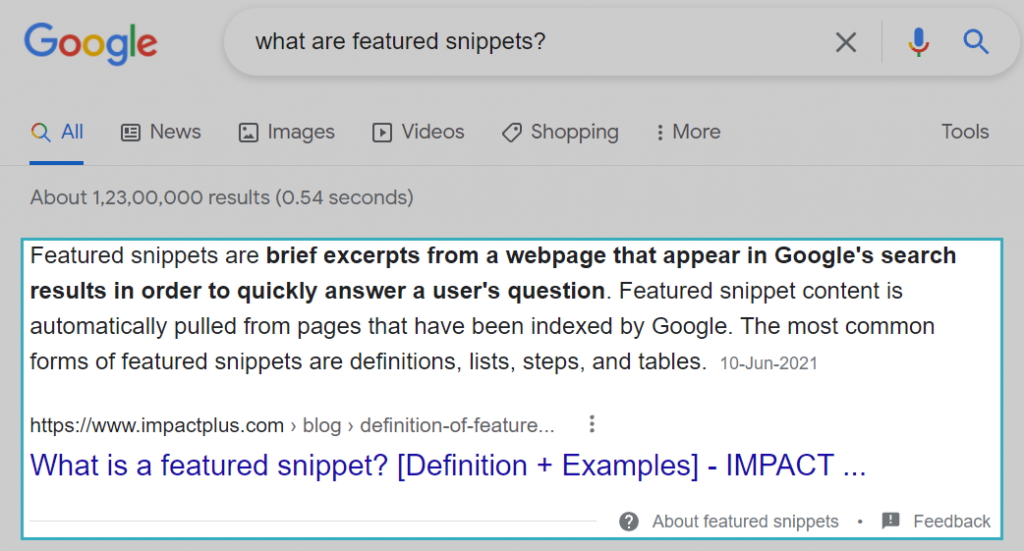
When you use structured data, you can get your pages to appear as rich snippets on the Google search results page. You also stand a chance to rank in the featured snippets, which are the first search result for a search query.
Here’s an example of a featured snippet for the query “what are featured snippets?”
How can you use structured data to make your search results appear as rich snippets?
You simply need to use a free schema markup generator tool to generate a code for you in the right format. You can choose which type of rich snippet code you want and the tool will generate it for you.
Some of the most popular types of markups are:
- Organization
- Local business
- Person
- WebPage
- FAQ
- Breadcrumb
- Article
- Event
- How to
- Logo
- Video
- Sitelinks
- Recipe
- Product
- Review
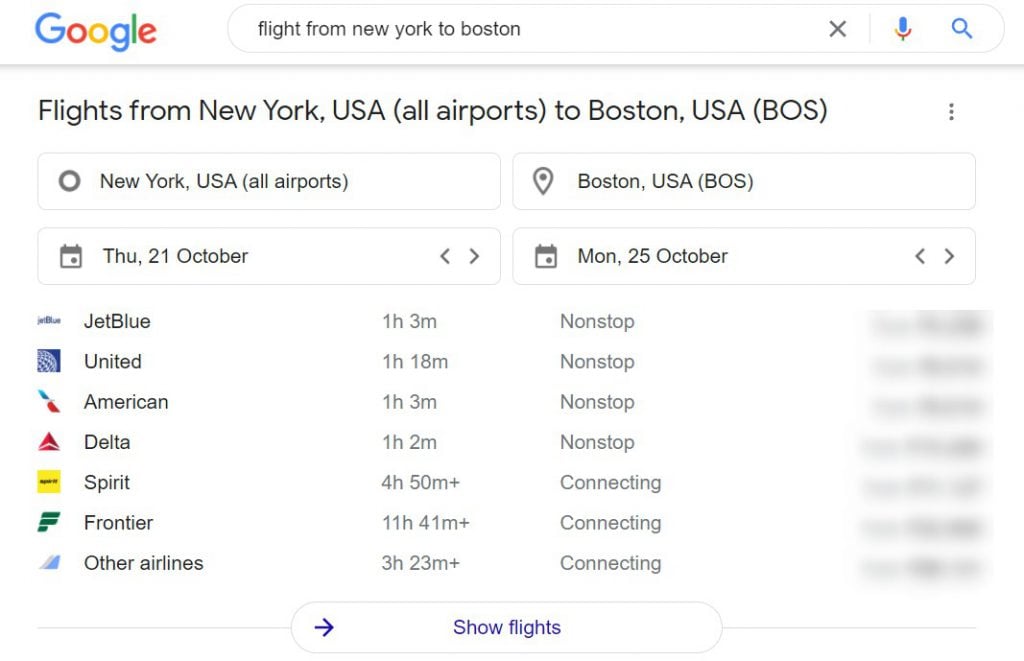
Then, you simply need to copy and paste this code into your site’s HTML code and you will be eligible for featuring as rich snippets.
8. Page Speed
Page speed is in the list of the top Google ranking factors because it directly affects user experience.
Page speed, along with responsiveness, and visual stability is a part of the Core Web Vitals report, recently added to theGoogle Search Console. Google checks the Core Web Vitals of a website to determine its user experience based on user interactions with the website.
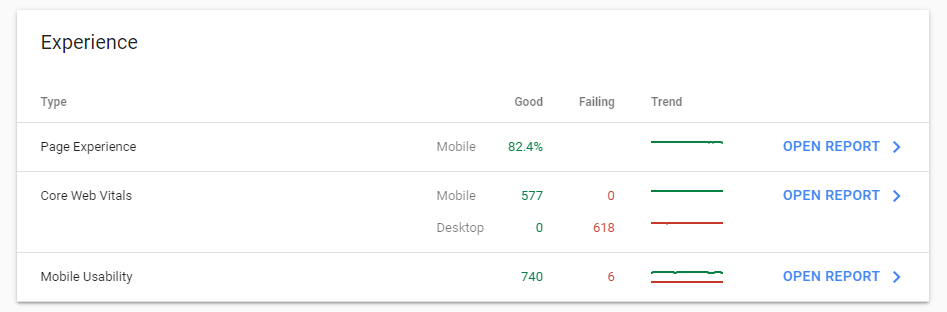
If your website loads slowly, a lot of people will simply bounce off your page and click on another search result. This, in turn, a lot of bad UX signals to Google showing that people are not liking your site.
How can you improve your site speed?
Here are some tips:
- Compress the file size for all visuals
- Avoid or reduce the number of redirects
- Use cache memory to store temp files
- Leverage a content delivery network (CDN)
- Clear and streamline your site code
- Optimize server response times

9. Website Security
Website security is one of the trust factors and directly impacts your SERP rankings. Google trusts sites with a valid SSL certificate more than those that don’t. It’s as simple as that.
Simply getting an SSL certificate can improve your rankings, so you should do that on priority. You can get HTTPS security directly from your web hosting provider or get an SSL/TLS certificate from Certificate Authorities.
10. User Engagement
Google determines user engagement based on a number of UX signals. If Google finds that you provide a good user experience, then your chances of ranking higher increase.
Google looks for the following metrics to determine engagement:
- Time on page
- Bounce rate
- Pages per session
The idea is that if a user finds your content useful, they will spend more time reading it and would also check out other related content.
The question is:
How can you ensure higher user engagement?
The answer is simple—create relevant and useful content, rich with engaging visuals, that meets the search intent.

Google Ranking Factors – A Complete List of 200 Factors
In this section, we will cover the entire list of 200 known Google ranking factors.
So, let’s get started.
Domain Ranking Factors
1. Your domain age: A domain’s age does not affect rankings a lot and even domains that are a few months old can rank high on SERP.
2. Keyword is in your domain: If you have a keyword in your domain, then it will act as a relevancy sign, even though it might not do much for boosting rankings.
3. Keyword is the first word in your domain: If you add your primary keyword as the first word in your domain it will definitely help more than simply adding a keyword in the middle or at the end.
4. Your domain registration length: If your domain is paid for in advance, then Google will consider it more legitimate than a domain that is due to expire in a few months.
According to Google:

5. Keyword is in the sub-domain: Having a keyword in your subdomain is another relevancy signal that does not affect rankings much, but still contributes.
6. Domain history: If a domain has been bought and sold many times, then Google will reset the site’s history and negate all previous backlinks. If there was a Google penalty that the domain had, then it will be carried forward to the new owner.
Check out this video by Google for more information about domain history and how penalties are transferred.
7. Penalized Whois owner: If the owner of a site is known to Google as a spammer, then Google will scrutinize other websites owned by the same person.
8. Public Whois instead of private Whois: As a general rule, it is best to keep your Whois information public and private Whois may be a signal that there is something to hide.
9. Country TLD extension: If your site has a country code TLD ( top-level domain), then it has slightly higher chances of ranking for searches within your country. However, it could also mean that it doesn’t rank as high for other regions.
Here’s an example that clearly shows this Google ranking factor at work.
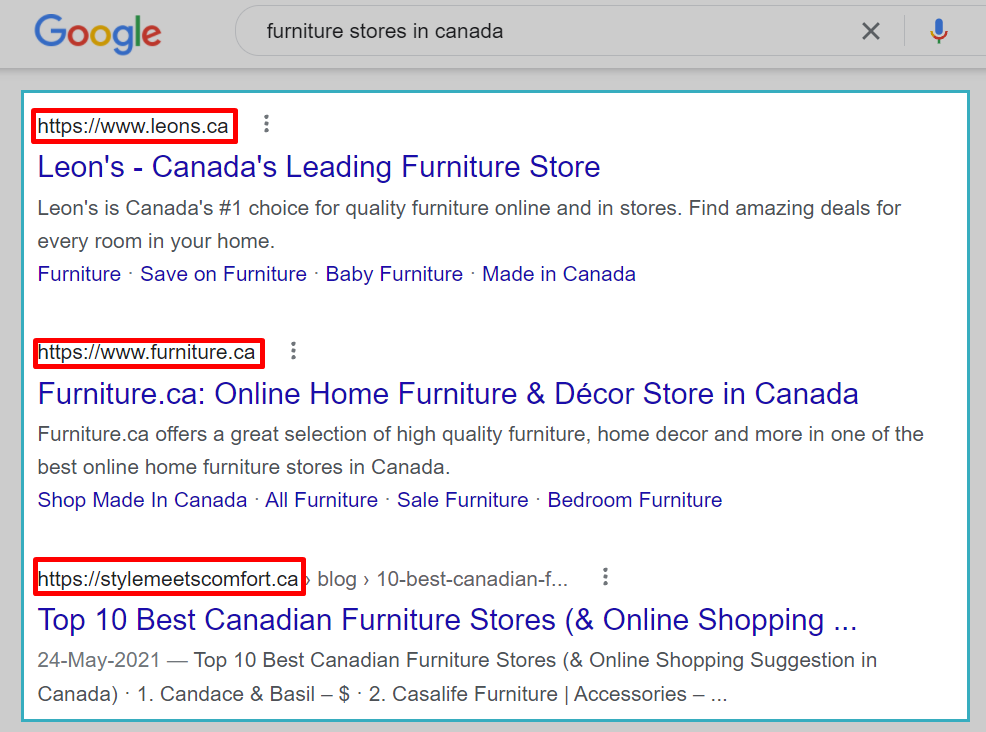
10. Exact Match Domain – This means having your exact match target keyword in your domain name. However, EMD or keyword domains only work in conjunction with other factors like a good user experience and relevant content.
Page-Level Ranking Factors
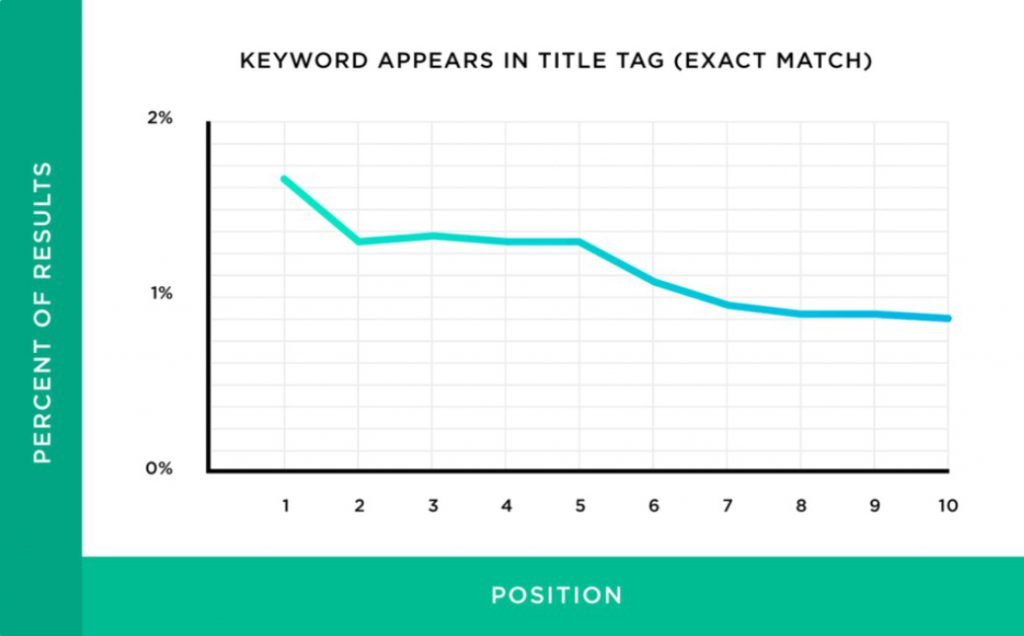
11. Presence of the keyword in the title tag: If you add your primary keyword to your title tag, it shows Google that your content is relevant for a particular search query and it improves your rankings.
Here’s an analysis by Backlinko that shows that having a keyword in the title tag is proportional to higher SERP rankings.
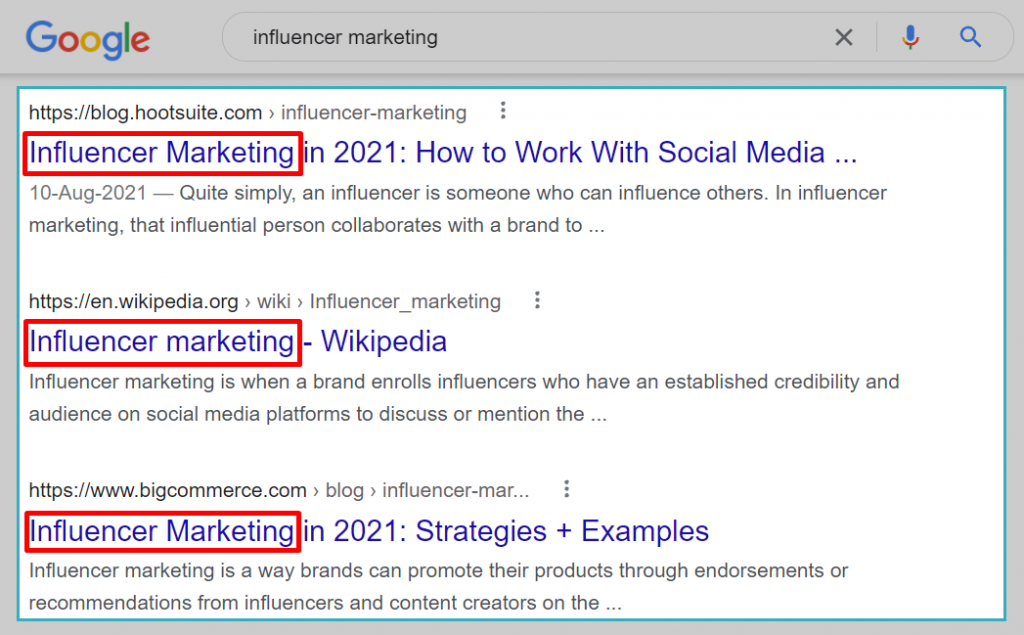
12. Having the keyword at the beginning of your title tag: This is even more effective than the previous point, as can be seen in the example below.
13. Keyword in your meta description tag: This is another important on-page SEO factor that Google uses to determine whether a piece of content is relevant to a particular search query. Adding relevant keywords to meta descriptions helps Google as it sends a relevancy signal.
In the same example as above, you will see that two of the three top-ranking posts have the exact keyword at the beginning of their meta descriptions.
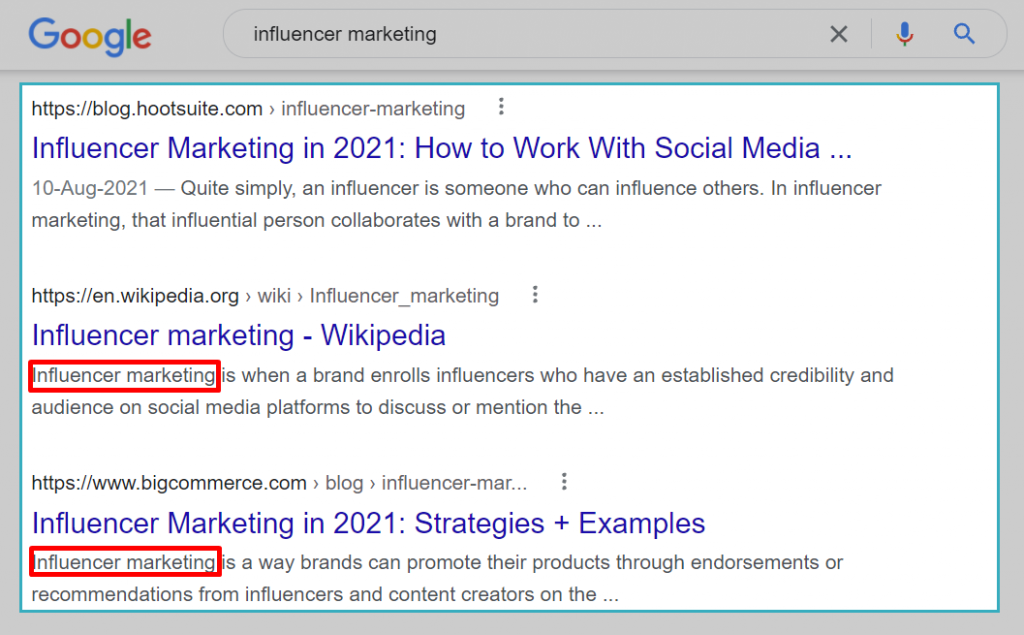
14. Presence of the keyword in the H1 tag: Another thing to cross off your on-page SEO checklist is to add your primary keyword in your H1 tag.
15. Keyword density: Your primary keyword should be present throughout your content and should have at least 1% density.
You can use a tool like TF-IDF to check your keyword density.
16. Content length: Longer content is generally considered more valuable and often ranks higher than shorter content. However, there is no guarantee that longer content will always rank as there are a lot of other Google ranking factors at play.
17. A linked table of contents: A linked ToC not only adds more structure to your content but also helps Google understand it better. And, if you know how search engines work, you know that the better Google understands your content, the higher its chances of ranking.
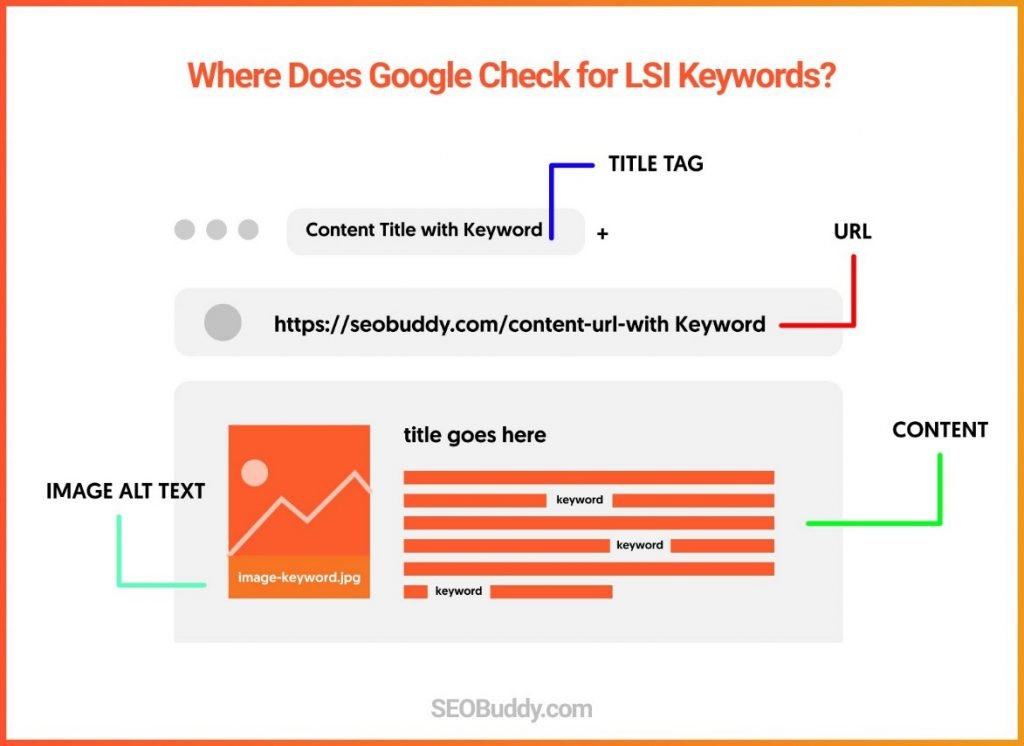
18. Presence of LSI keywords: Latent Semantic Indexing keywords or LSI keywords are variations of your primary keyword that provide more information about the content. Google looks for LSI keywords to better understand your content and index it.
19. LSI keywords in title tags, URLs, and meta descriptions: Google checks for LSI keywords in certain places within your content. You should add LSI keywords to your meta descriptions, URLs, and title tags to get the best results.
20. In-depth quality content: This is probably one of the most important Google ranking factors. If your content covers a topic in detail and provides all useful information, then it has a higher chance of ranking well on SERP.
21. Useful content: Just creating quality content is not enough if it is beyond the understanding of an average reader, you also need to make it useful and easy to understand.
22. Page loading speed using HTML: Page speed is one of the most known and important Google ranking factors and Google can easily assess your speed via your HTML code. After all, Google would not want to direct its users to slow or unresponsive sites.
To check your page speed, you can use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool.

23. Page loading speed tested on Chrome: Google also checks a page’s loading speed via Chrome, thus making it another one of the Google ranking factors.
24. Core web vitals: Google’s core web vitals report analyses a website’s speed, responsiveness, and visual stability. The higher the score, the better.
25. No duplicate content on the same site: Make sure that your site has no duplicate or similar content, as it can adversely affect your rankings.
26. Proper use of rel=canonical tag: If used right, this tag can help you avoid Google penalties for duplicate content.
27. Image optimization: Add relevant keywords in your image alt text, file name, and descriptions to send relevancy signals to Google.
28. Content recency: After the Google Caffeine update, recency has been added to the list of Google ranking factors. The general rule is—the newer, the better.
29. Page age: Although recency matters, an old page that is regularly updated may outperform newer pages.
30. Level of content updates: The number of edits or updates made to a page also matter. Pages in which entire sections were updated are considered fresher.
31. Historical page updates: The number of times a page was updated in the past also counts as one of the Google ranking factors to check freshness and recency.
32. Presence of the keyword in H2 and H3 tags: Add your primary keywords in H2 and H3 tags of your content to send relevancy signals to Google.
33. Presence of keyword in the first 100 words: This is one of the important Google ranking factors as the presence of a keyword in the first few lines shows Google what your content is about.
34. Grammar and spelling: This is not one of the most important Google ranking factors, but still an indication of quality content for both search engines and readers.
35. The originality of the page’s content: Syndicated content may not rank as high as original content and may not even get indexed at all.
36. Entity match: If your page’s content matches the entity that someone is searching for, then it might get a ranking boost.
37. Number of outbound links: Do not add too many Dofollow links on one page as that would hurt your PageRank.
38. The quality of outbound links: Link to authoritative websites in your niche to send trust signals to Google.
39. The Theme of outbound links: Make sure that your outbound links are to similar sites and content that are relevant to your content.
40. Mobile usability and optimization: Google’s mobile-friendly update rewards pages that mobile users can easily access and use.
41. Hidden content on mobile: If you have any hidden content on mobile devices then chances are that it might not get indexed. So, make sure that all critical content is visible.
42. Page optimized for mobile: One of the important Google ranking factors is whether your site renders well on mobile devices or not. Use a mobile-optimized website theme to ensure that your site is mobile-friendly.
43. Presence of multimedia: The presence of visuals on a page sends quality signals to Google and is one of the important Google ranking factors.
44. Presence of helpful supplementary content: Supplementary content like currency converters, calculators, and other tools improves a page’s quality in the eyes of Google.
45. Content hidden behind tabs: Such content may not be indexed and probably will not show up in search snippets.
46. No. of internal links pointing to the page: The more links that point to a page, the more it is considered useful and related to the content on other pages.
47. Quality of the internal links: Internal links from popular or authoritative pages have more impact than those with no PageRank.
48. Presence of broken links: This is another one of the important Google ranking factors. Too many broken links may be a sign of a neglected or abandoned site.
49. The reading level of the content on a page: The golden rule is to find a balance between quality and ease of understanding. Reading level should be low enough for everyone to understand, but not so low that it is considered a low-quality content mill.
To check your reading level you can find the readability score on the Hemingway Editor. A score of 5-8 is considered good.
50. Presence of many affiliate links: Affiliate links only matter when there are too many of them because then that draws Google’s attention to your site and it has to go through more scrutiny.
51. Presence of many HTML errors: Lots of HTML coding errors indicate a poor quality site, which can adversely affect your rankings.
52. Authority/trust-level of the domain: This is one of the most important Google ranking factors as Google prefers authoritative sites over others.
53. Authority/trust level of the page: Similar to the authority level of a domain, the authority of pages also factors in when deciding SERP rankings.
54. PageRank: Pages that get a lot of backlinks have a higher authority than pages that don’t. So, one off-page SEO best practice that you should follow is to try and get more backlinks from popular pages to boost your trust signals.
55. Length of URL: As a general rule, keep your URLs short and crisp, and add your primary keywords in URLs.
56. Closeness of URL to the homepage: A shorter URL path usually results in a boost in authority than URLs buried deep within a site’s architecture.
57. Presence of keyword in URL: URLs with keywords send relevancy signals to Google and help boost rankings.
58. Opinion of human editors: Google has filed a patent that allows editors to influence SERP rankings.
59. Relevance of page category: A page within the relevant category sends a relevancy signal to Google.
60. Content user-friendliness and readability: Content that is easy to read encourages people to stay and read for longer, which sends good UX signals to Google.
61. Priority of the page in the sitemap.xml: Higher priority pages may get a ranking boost over low priority pages.
62. UX signals from a site ranking for related keywords: If a site ranks for multiple related keywords, Google considers it useful and relevant.
63. Citing references and sources: These send a quality signal to Google showing that your content is well-researched and of high quality.
64. Use of a user-friendly layout: A good layout allows users to find exactly what they are looking for quickly and easily.
65: URL string in Google search results: Google checks URL strings to identify categories and determine what a page is all about.
66. Parked domains: The search visibility of parked domains is lower than regular ones.
Backlink Ranking Factors
67. Age of linking domain: Backlinks from aged domains cast more powerful votes of confidence than those from new domains.
68. Number of referring domains: The number of unique domains that link to your site is one of the important Google ranking factors.
69. Number of links from separate c-class IPs: This shows the breadth of websites linking to your site, which can positively affect rankings.
70. Number of referring pages: The more pages that link to your site, the better.
71. Anchor text of backlinks: This is another one of the important Google ranking factors. Anchor text should always be relevant to the link it is directing to and should preferably be keyword-rich.
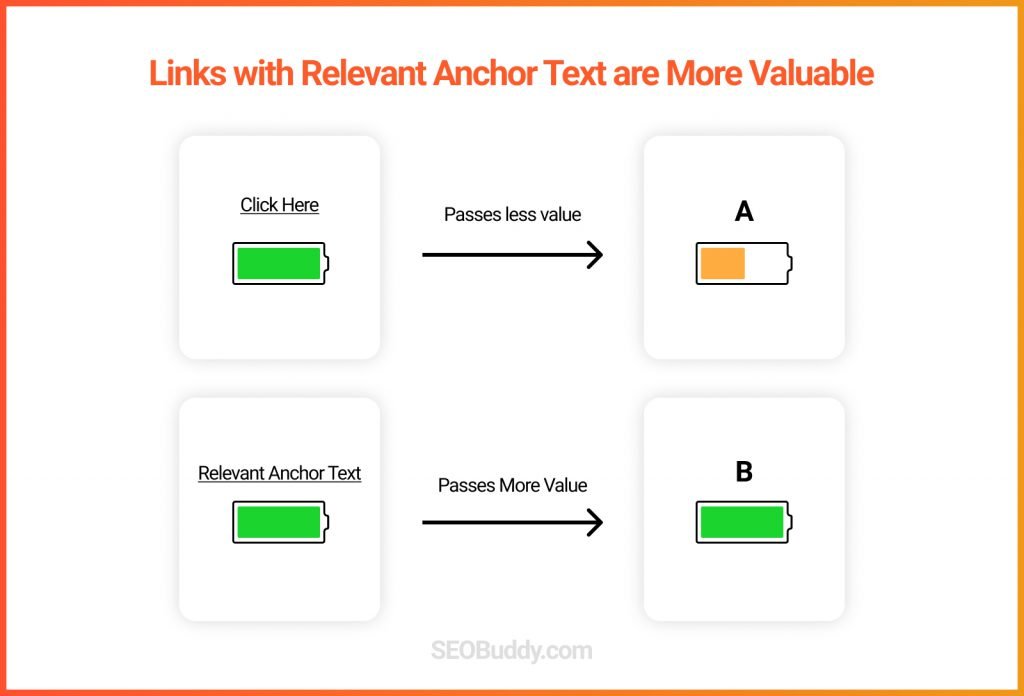
72. ALT tag of image links: Alt text sort of acts like an anchor text for images and contributes to higher rankings.
73. Number of links from .edu and .gov domains: This is one of those Google ranking factors that Google denies but SEO professionals still think is important.
74. Trust factor of linking page: The PageRank of a linking page is an important factor that determines how impactful backlinks from such pages will be.
75. Trust factor of linking domain: Backlinks from authoritative websites hold more weight than backlinks from low authority sites.
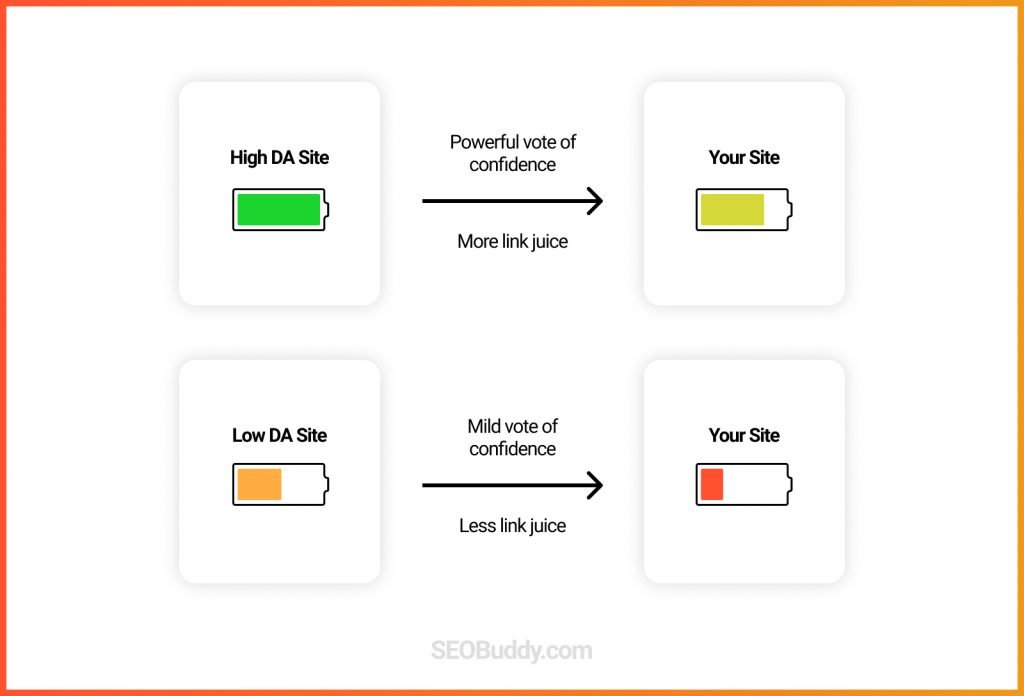
76. Presence of links from competitors: Links for sites ranking for the same keywords show the value of your content and hold a lot of weight.
77. Number of links from expected sites in your industry: Google will trust your site more if you get backlinks from the expected sites in your niche.
78. Links from bad neighborhoods: Backlinks from bad link neighborhoods may hurt your site and should be avoided.
79. Number of links from ads: Links from ads should be nofollow links and if they are not Google will anyway filter them out.
80. Presence of nofollow links: This is one of the most controversial Google ranking factors as some argue that it affects rankings, while others say that Google completely ignores such links.
81. Diversity of link profile: In general, links coming from diverse sources is better than too many links from the same site.
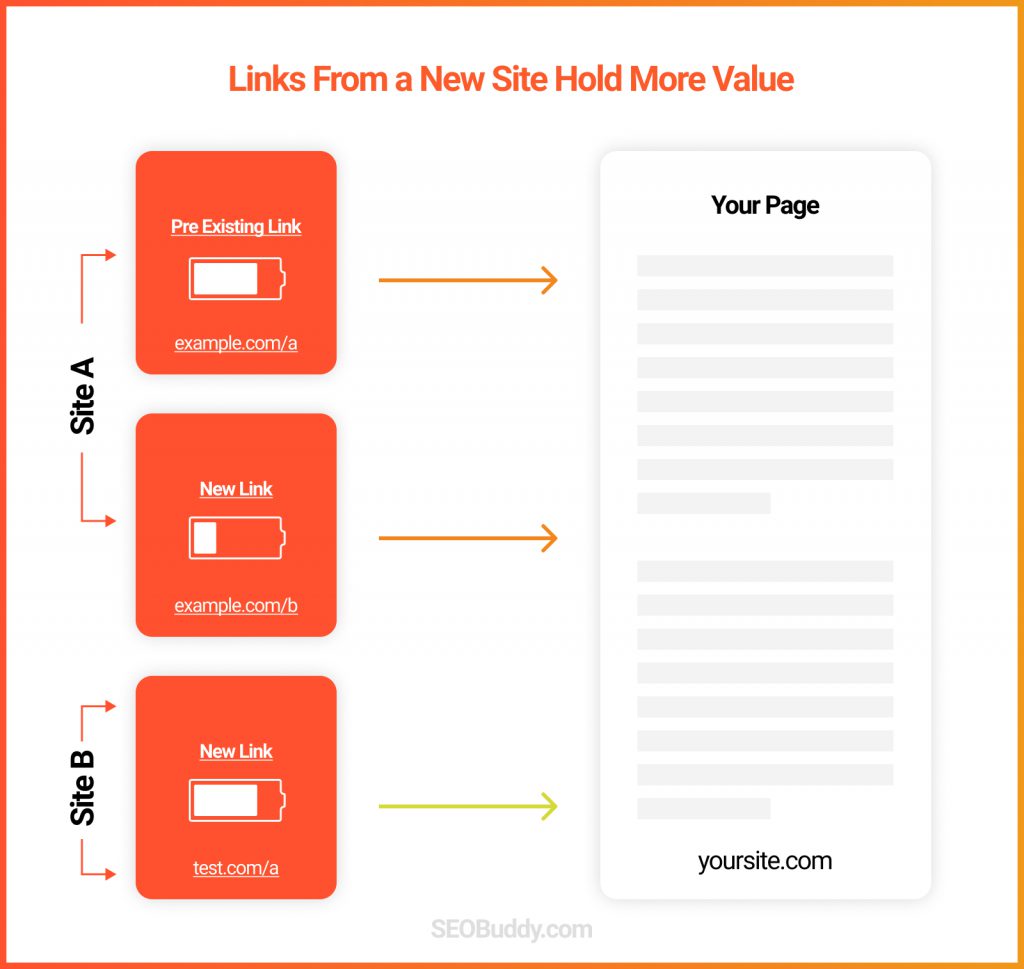
82. Links inside the main content: Backlinks that are placed in the main content hold more value than those hidden in sidebars or other places.
83. Presence of more follow links than sponsored or UGC: Follow links are treated as more important than links tagged as “rel=sponsored” or “rel=UGC”.
84. Lots of backlinks to URL with 301 redirects: Avoid backlinks coming from 301 redirects, as they may dilute some of your PageRank.
85. The text that appears when you hover over a link: The link title attribution may count as a relevancy signal, but is not very important.
86. Link location in content: Links that are towards the beginning of the main content on a page hold slightly more weight than links that are placed towards the end.

87. Links from relevant domains: Backlinks from sites in your niche are more powerful than links from unrelated sites.
88. Links from relevant pages: Similarly, links from similar or topically-relevant pages hold more weight than those from unrelated pages.
89. Presence of your page’s keyword in the title of the linking page: If a page that links to your page has your keyword in the title, then Google gives it more prominence.
90. Natural rate of growth in the number of links: Increase in growth of links shows that a site is growing in popularity and is also a signal for freshness. Similarly, negative growth is bad for rankings.
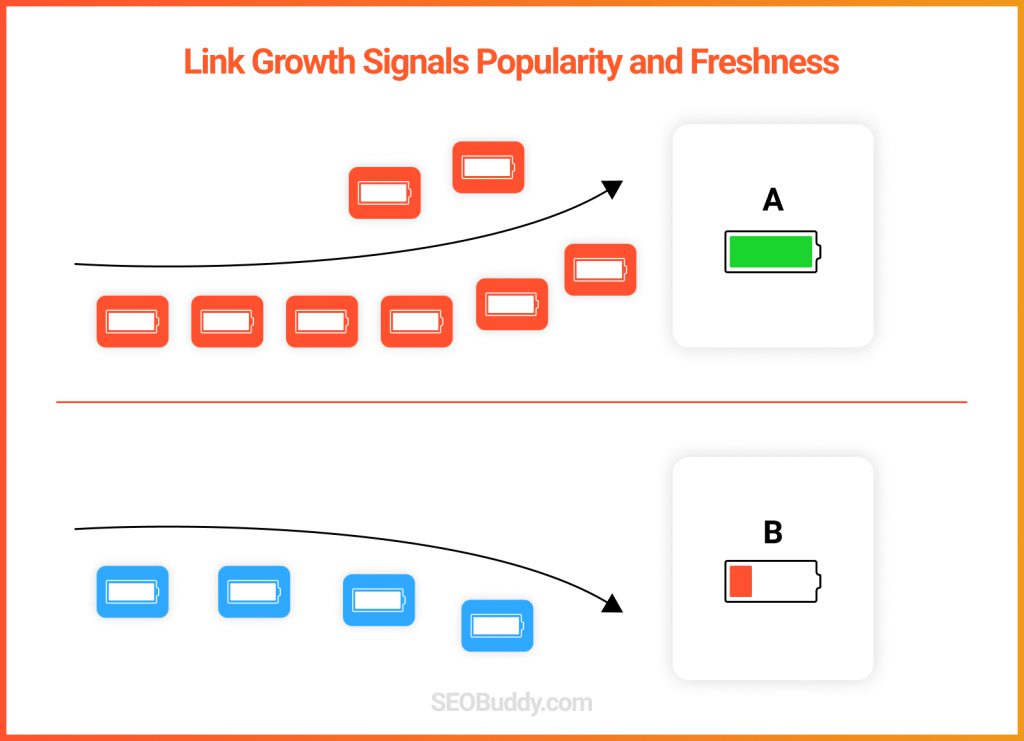
91. Spiky and unnatural rate of growth in the number of links: An unnatural growth in links, however, may signal spam or link farms, thus adversely affecting rankings.
92. Links from top resources on a certain topic or hubs: Such links are given more importance and are one of the important Google ranking factors.
93. Number of links from sites that are considered authority sites: The higher the number of backlinks from authoritative sites, the better.
94. Linked as a source in a Wikipedia article: These are usually nofollow links, but some SEO professionals consider that these signal trust and authority for your site.
95. Words around your backlinks: These words or co-occurrences help Google understand what your page is about and give more context.
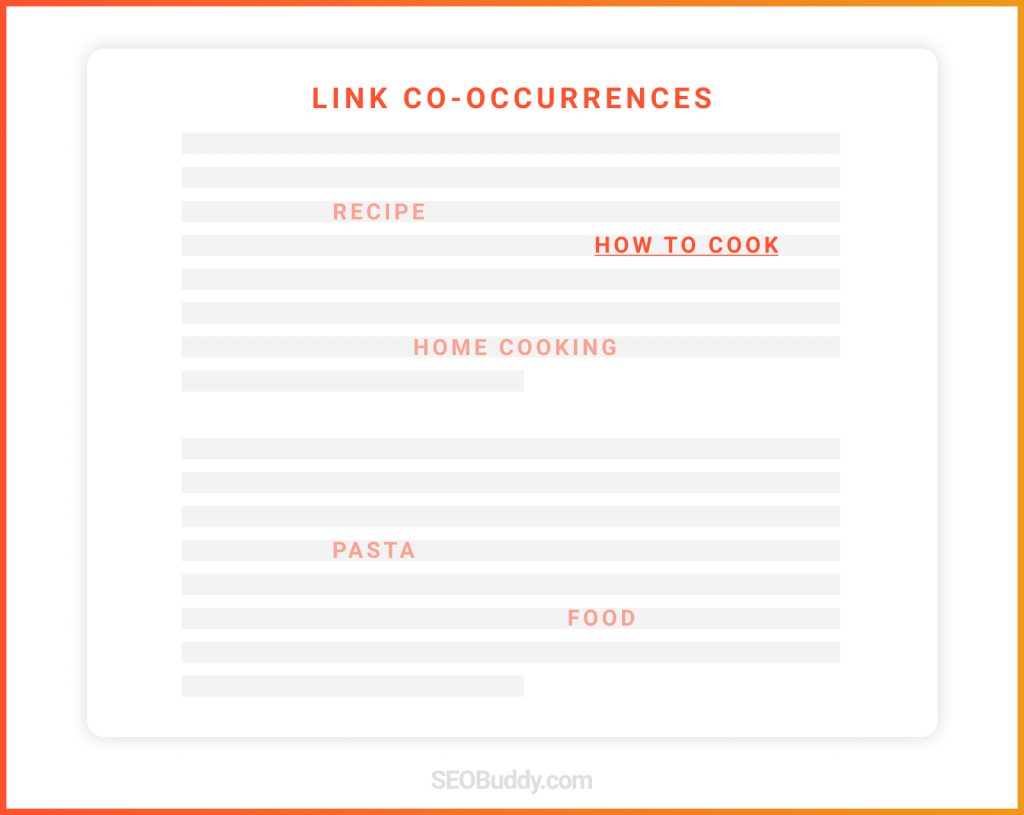
96. Backlink age: Generally, older links have more value than newer ones.
97. Links from real sites vs fake blogs: Needless to say, links from real sites value more than those from fake blogs.
98. Natural link profile: A natural link profile is more valuable than an unnatural one built using black hat SEO tactics.
99. Excessive reciprocal links: Google considers excessive reciprocal links as spam or a link scheme, which is bad for your site.
100. Links in real content vs. UGC: Google can distinguish between these two types of links and holds links from real content in higher regard.
101. Backlinks from a page with a 301 redirect: Links from a 301 redirect may lose some value or link juice.
102. TrustRank of linking site: A high TrustRank site may pass more of that trust to your site
103. Fewer outbound links on linking page: Backlinks from pages with a few links are better than links from pages with too many outbound links.
104. Links in real content vs links in forums: Links from forums are not as important as links from real content.
105. Word count of linking content: A link from long-form content holds more value.
106. Quality of linking content: Links from poor-quality content are not as important as links from high-quality content.
107. Sitewide links = one link: Sitewide links are compressed and counted as a single link.
108. Internal link anchor text: This can be another relevancy signal, but is not as important as external links.
109. Structured Data: This is one of the top Google ranking factors as it can help your page appear as rich snippets on SERP and get more clicks.
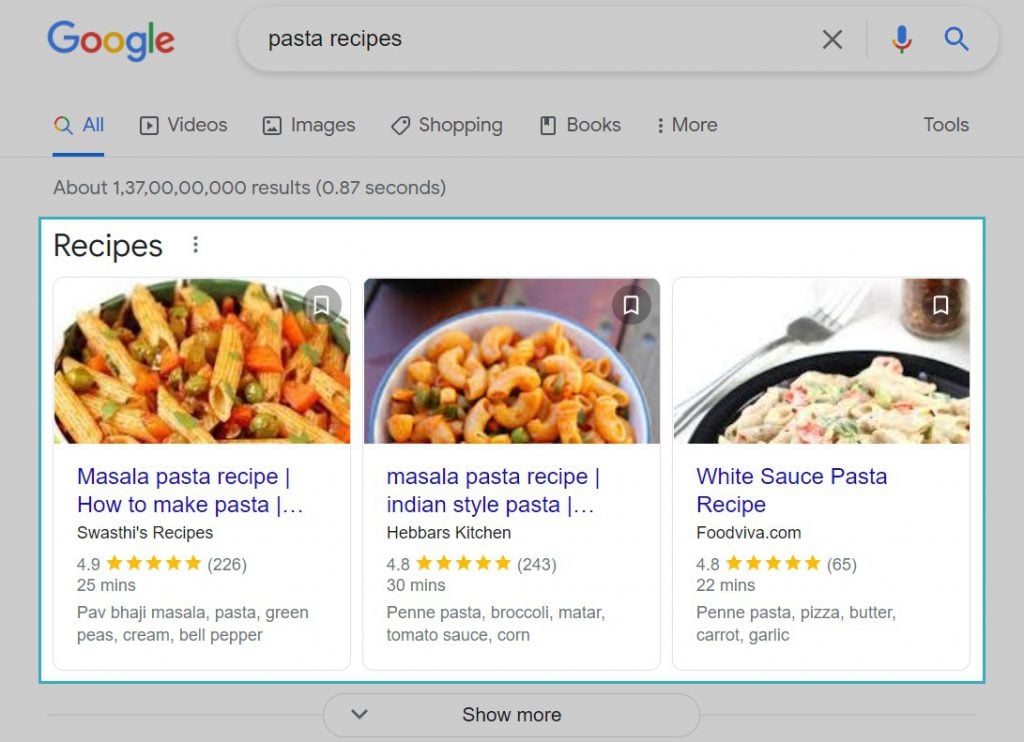
Here’s an example of how rich snippets appear on SERP.
Site-Level Ranking Factors
110. Presence of a contact us page: Google prefers and trusts sites that provide sufficient contact information.
111. Content on site provides value or new insights: This is one of the most important Google ranking factors, so make sure that you consistently publish valuable content.
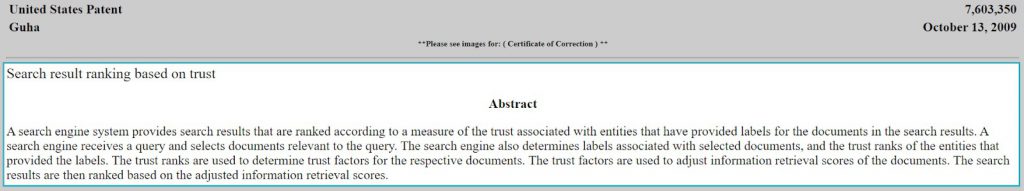
112. TrustRank: This is another one of the most important Google ranking factors and a patent filed by Google in 2009 confirms this.
113. Website updates for freshness factor: Regular site updates add to the site’s freshness, which Google considers as one of the important ranking factors.
114. Site architecture: Having a clean site architecture helps Google crawl, understand, and index your pages. The better Google understands your content, the higher your chances of ranking.
115. Presence of a sitemap: Similarly, a sitemap further boosts Google’s ability to understand and index your pages.
116. Long-term site downtime: Too much downtime may adversely affect your rankings.
117. Location of server: Server location affects how your site ranks in location-specific searches. If your server is located in the US, your site may get a ranking boost for US-specific search queries.
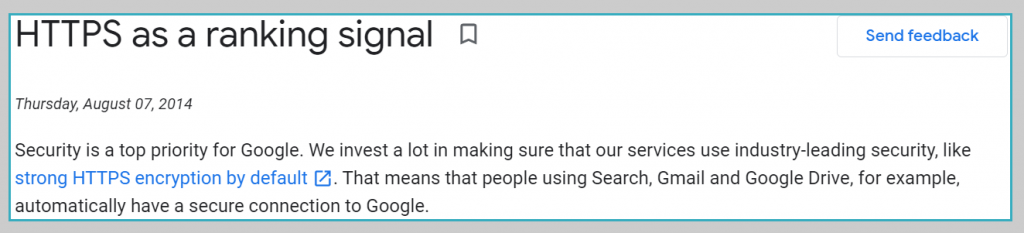
118. HTTPS/SSL certificate: Google considers sites with HTTPS or an SSL certificate as more secure and prefers these sites over non-secure ones.
119. Presence of legal pages (T&C and privacy policy): These pages tell Google that your site is trustworthy.
120. Unique metadata: Make sure that your site has unique metadata, as duplicate information can hurt your page’s search visibility.
121. Use of breadcrumb markup: This is one way of making your site architecture more user-friendly.
122. Site-wide mobile optimization: This is one of the top Google ranking factors as it can directly impact your site rankings. Google prefers sites that are mobile-optimized over those that aren’t.
123. User-friendliness (usability and interactiveness): A user-friendly site will have a lower bounce rate and good user engagement metrics, thus, better rankings.
124. User reviews: Positive user reviews improve your brand’s reputation and that positively affects rankings.
125. Site reputation: Your overall site reputation matters and is one of the off-page SEO factors that affect rankings.
126. RankBrain: It is Google’s AI algorithm that measures how users interact with the search results. This information is then used to rank the search results. User interaction is important not just for Google, but most search engines work in a similar manner.
127. The organic click-through rate for the exact keyword: This is another one of the top Google ranking factors. The more people click on your organic search results for the exact keyword the more Google will find it relevant and useful.
128. Organic click-through rates for all ranking keywords: Organic CTR for other ranking keywords is also important.
129. Dwell time: The more time a user spends on your website, the more Google considers it as relevant.
130. Bounce rate: The lower the bounce rate for your website, the better. A high bounce rate is a signal for poor user experience and should be avoided.
131. Total direct traffic: Google considers sites that get high direct traffic as high-quality sites and prefers them over others.
132. Percentage of repeat visitors: The more repeat visitors a site gets, the more relevant and useful it is considered by Google.
133. Blocked sites: Google’s Panda update used this as a quality signal and Google may still use some variation of it in its ranking factors.
134. Pogo sticking: If a large number of visitors click on other pages on the SERP after clicking or visiting your page, then your rankings may significantly drop.
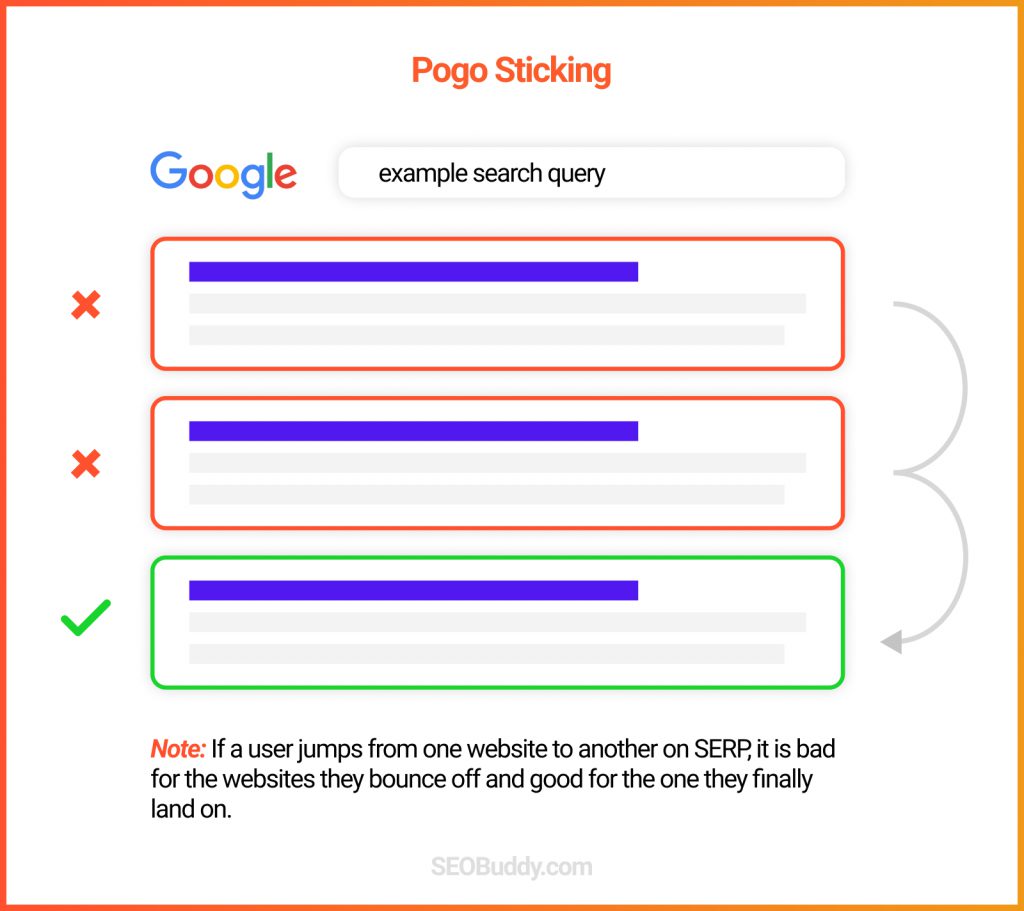
135. Page frequently bookmarked by Chrome users: Pages that are frequently bookmarked are considered useful and may get a ranking boost.
136. The number of comments on a page: Pages that get tons of user comments may be considered good as people actively interact with those pages.
Special Google Algorithm Rules
137. Need for diversity in the SERP: Google may present diverse search results for ambiguous keywords that can mean different things like “Ruby”.
138. Need for freshness in the SERP: Fresh content may get priority for certain search queries that deserve freshness.
139. Browsing history of a user: If a user visits certain sites more frequently then those sites will get a ranking boost for that particular user.
140. Search history of a user: A user’s search history affects their search results for future searches.
141. Featured snippets: To rank in featured snippets you need succinct answers, good formatting, page authority, and HTTPS.
142. Geo-targeting: Local server IPs and country-specific TLDs get a preference for local search queries.
143. Safe search: For users who have turned the safe search mode on, adult content or content with curse words will not appear in the search results.
144. YMYL keywords: Google maintains higher content quality standards for “your money” or “your life” keywords.
145. Legitimate DMCA complaints: Pages with DMCA complaints are downranked by Google.
146. Need for domain diversity in SERP: After a recent update, Google shows search results from more diverse domains than showing multiple results from the same domain.
147. Transactional searches: For certain types of transactional keywords, Google shows different search results than normal ones. For example, when you search for flight tickets, you will see an option of booking the flights directly from the search results.
148. Local search results: Google prefers to show local search results for local searches.
149. Top Stories box: For certain keywords, Google triggers a Top Stories box that appears different from normal search results.
150. Presence of big brands with relevant content: Google often gives preference to big brands for certain keywords.
151. Results optimized for Google Shopping: For certain types of keywords, Google shows Google Shopping results first.
152. Image results: For some keywords, Google Images appear first in the search results.
153. Branded search: For brand-specific keywords, Google shows several results from the same domain.
154. Easter eggs: For some specific keywords Google shows a completely unique search result like a playable game or an animation. These are just fun elements that Google launches from time to time.
155. Spammy queries: For very spammy queries, a special Google algorithm called Payday Loans Update gets triggered and clears the query.
Brand Signals
156. Branded anchor text: Using a brand name as anchor text is a strong brand signal.
157. Brand searches: If people specifically search for your brand, then Google understands that your brand is legit. The more brand searches there are for your brand, the better.
158. Brand + keyword searches: If many people search for your brand along with a specific keyword, then your brand will get a ranking boost for the keyword in non-branded searches as well.
159. Facebook page with likes: A brand that has a Facebook page that gets lots of likes then Google will take that as a brand signal and regard that brand highly.
160. Twitter profile with lots of followers: Such a brand is considered popular and Google regards it as such.
161. An official LinkedIn company page: Good and legit brands should have an official LinkedIn page, otherwise Google will doubt if the business is even real.
162. Known authorship: Verified profiles of known personalities get a preference over unknown authors.
163. Real social media accounts: Google also checks the legitimacy of branded social media accounts and can identify fake accounts and businesses.
164. Top Stories brand mentions: Some really big brands often get mentioned in Google’s Top Stories box.
165. Unlinked brand mentions: While it is always better to get backlinks from brand mentions, Google does consider unlinked mentions as brand signals.
166. Physical store locations: Any legit, big business usually has physical stores as well. Google considers this information as a strong brand signal.
On-Site Webspam Ranking Factors
167. Low-quality content: After the Panda update, Google has started penalizing content farms and sites with poor-quality content.
168. Links to bad neighborhoods: Linking to spammy or bad sites may hurt your search visibility.
169. Multiple or sneaky redirects: Using such malpractices can get your site penalized or even de-indexed.
170. Distracting ads and pop-ups: These signal a low-quality site and are one of the Google ranking factors that can directly affect your search rankings.
171. Interstitial pop-ups: Google may penalize your site if you show intrusive pop-ups that block the main content.
172. Over-optimization: Keyword stuffing can be considered a sign of a low-quality or spammy site, and you may be penalized for it.
173. Gibberish: Google is capable of identifying and filtering out gibberish content.
174. Doorway pages: Google does not like sites that show a different page at first and then redirect users to another page.
175. Above-the-fold ads: While it is not wrong to place a one-off ad above the fold, it becomes a problem when the ads take so much space that no main content is visible above the fold. Google addressed this in its Page Layout Algorithm.
176. Cloaked affiliate links: Using too many hidden affiliate links can cause a Google penalty.
177. Low-value content sites: Google does not like sites that put revenue above helping their users and churn out low-quality content.
178. Affiliate sites: Affiliate sites are put under more scrutiny by Google than regular sites.
179. Auto-generated content: If Google finds signs that your site is using computer-generated content, then it might penalize or even de-index your site.
180. Nofollowing all outbound links: Excess PageRank sculpting or nofollowing outbound links can be considered a sign of cheating the system and can be penalized.
181. Keyword stuffing in meta tags: Google can identify and penalize excessive meta tag spamming.
182. IP addresses flagged as spam: If one site on a server is flagged as spam, then all sites on that server will get affected.
Off-Site Webspam Ranking Factors
183. Hacked site: Google de-indexes any sites that it thinks are hacked.
184. An unnatural influx of links: Google can identify black hat link-building schemes and penalize websites that see an unnatural link growth.
185. Penguin penalty: After Google’s Penguin update, a lot of sites were penalized for bad backlinks. Such sites suffer from poor search visibility.
186. Lots of low-quality links: A poor backlink profile may signal black hat practices and attract a penalty.
187. Links from irrelevant sites: Irrelevant backlinks from unrelated sites may attract a Google penalty.
188. Unnatural links warning: If you ever receive a warning like that, work on it immediately or else yoru rankings will drop.
189. Low-quality directory links: Too many backlinks from low-quality directories can do more harm than good.
190. Widget links: Avoid links that are automatically generated when a user downloads and installs a widget.
191. Links from sites with the same server IP: This signals the presence of a blog network and Google frowns on such link-building practices.
192. Using “poison” in your anchor text: This is considered unethical and can hurt your website’s rankings.
193. Unnatural link spike: Google devalues unnatural links to a website.
194. Links from articles and press releases: Though it is a legitimate link-building tactic, it has been overused to the extent that it is sometimes considered a link scheme.
195. Manual actions: Google can often take manual actions against unethical SEO practices.
196. Selling links: If you are caught selling links then you will attract a Google penalty.
197. Google Sandbox: New sites that get a sudden spike in links are put in Google Sandbox that temporarily hurts their search visibility.
198. Google Dance: Google often shakes rankings temporarily to figure out whether a site is trying to game the system.
199. Disavow tool: You can use a disavow tool to remove harmful backlinks that have or may cause a penalty.
200. Reconsideration request: After removing harmful backlinks you can send a reconsideration request. If it is accepted, then it will remove the Google penalty and help improve your search visibility and rankings.
201. Temporary link schemes: These include adding spammy links temporarily and then removing them. Google can identify and penalize such schemes.

Now it’s time to discover the other 102 steps that will get more organic traffic flowing to your website. Get the SEO Checklist here.
Want to get a sneak peek of what it looks like?
Enter your email and get a free demo version of the SEO Checklist.
FAQs
1. What are the most important Google ranking factors?
The top ten most important Google ranking factors are:
- Content quality
- Keyword optimization
- Organic click-through-rate
- Authoritativeness and Expertise
- Mobile-friendliness
- Backlink profile
- Structured data
- Page speed
- Website security
- User experience
2. What are the 200 Google ranking factors?
Google uses a combination of over 200 ranking factors to determine which results to show first. These 200 Google ranking factors can be divided into the following categories:
- Domain ranking factors
- Page-level ranking factors
- Backlink ranking factors
- Backlink ranking factors
- User interaction factors
- Special Google algorithm rules
- Brand signals
- On-Site webspam factors
- Off-Site webspam factors
If you feel overwhelmed by the long list of Google ranking factors, you can download our SEO checklist. It will help you cover all important pillars of SEO, without wasting too much time on factors that don’t make much of a difference.
3. Is Google E-A-T actually a ranking factor?
EAT stands for expertise, authority, and trust. EAT is not one of the direct Google ranking factors. However, Google uses a combination of ranking factors to determine a website’s expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
So, in a way, EAT is the combination of multiple Google ranking factors working together.
4. What does Google use for ranking?
Google uses over 200 different ranking factors to determine each page’s SERP (search engines results pages) ranking.
However, not all of these Google ranking factors contribute equally. In fact, most of these Google ranking factors do not even have a direct impact on SERP rankings.
There are certain Google ranking factors that hold the most weightage. These factors include:
- Content quality
- Keyword optimization
- Organic click-through-rate
- Authoritativeness and Expertise
- Mobile-friendliness
- Backlink profile
- Structured data
- Page speed
- Website security
- User experience
5. What are the most important factors of a page quality rating?
Here are some of the most important factors for a page quality rating:
- EAT (expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness)
- The purpose of a page
- Quality and quantity of content
- Clear and accurate website information
- Overall website popularity and reputation
Conclusion
This is quite a long list of Google ranking factors—too long to memorize and remember.
So, what can you do?
You can use our detailed SEO checklist to make sure that you don’t miss any important aspects of SEO. Our checklist will help you focus your efforts only on the important Google ranking factors while ensuring that every base is covered.
And if you want to study the Google ranking factors in detail, you can always come back to this post and use it as a reference and a guide.
Have any further questions? Feel free to drop us a line in the comments section.









Every factors you mentioned is very effective. thanks for this great article
Very Nic Blog thank you
Thanks for sharing nice post on google ranking factors