13 Must-Use Google Search Operators for SEO
Google search operators are a combination of words and symbols that help Google improve the search engine results.
If you’ve been in the SEO game for a long time, you might already know some or more search operators.
But how do you remember all the functional Google search operators that can change the way you dig into SERP?
Fret not.
We’ve compiled a list of Google search operators that you can download (link in conclusion).
However, it isn’t just about memorizing the search operators; the real catch is to know how to use them. And more importantly, where to use them.
But the advanced Google search operators also have their own place in the SEO tools ecosystem.
While most SEOs only know basic operators and their limited uses, we’ve listed the most advanced as well as basic search operators along with actionable tips to help you win the SEO game.
Here we go.

13 Functional Google Search Operators in 2022
Following are the working and most useful Google search operators for 2022.
1. Quotes (“search term”)
Using quotes around the term you want to search will get you exact match search results instead of the broad match results you’d get otherwise. It’s the most popular Google search operator that even many non-SEOs are familiar with.
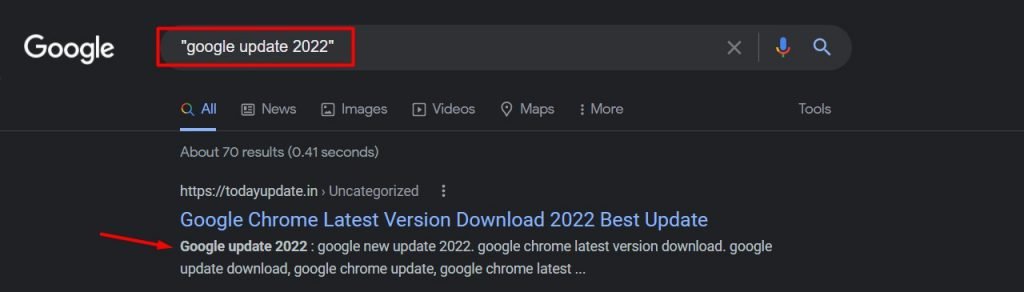
2. And, Or
Search for X and Y and you’ll get results related to both X and Y. Whereas if you search for X or Y, the results will include either X or Y. Also, note that you can use the pipe (|) instead of “or” to get the same results.
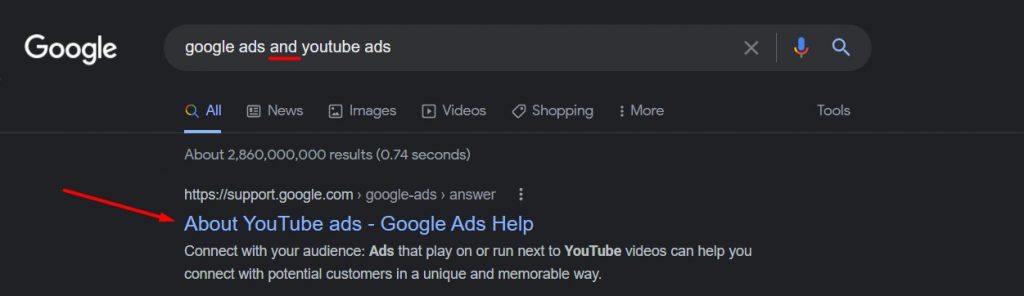
3. Exclude Words (-)
For Google search, the minus sign acts as an exclusion command, making it one of the most used basic search operators.
You can command Google search to exclude the words you don’t want to appear in your search results with this exclusion symbol.
For example, if, for any reason, you wish to search for “backlinking techniques” but don’t want “blog commenting” in your search results, this is what you’d search for:
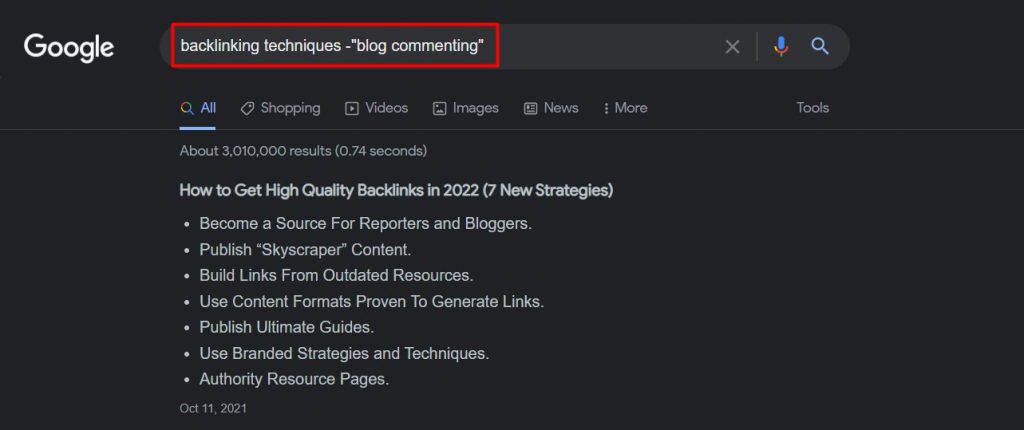
4. Wildcard (*)
The asterisk symbol in a search box represents a blank space that can be filled by any word, number, or term.
Basically, this Google search operator tells Google to fill in the blank by itself.
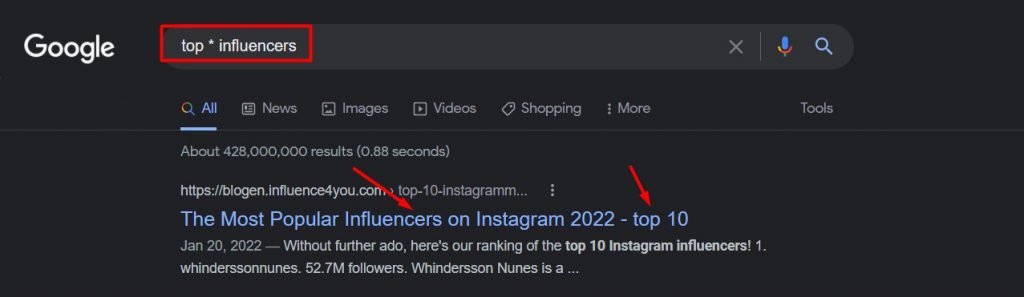
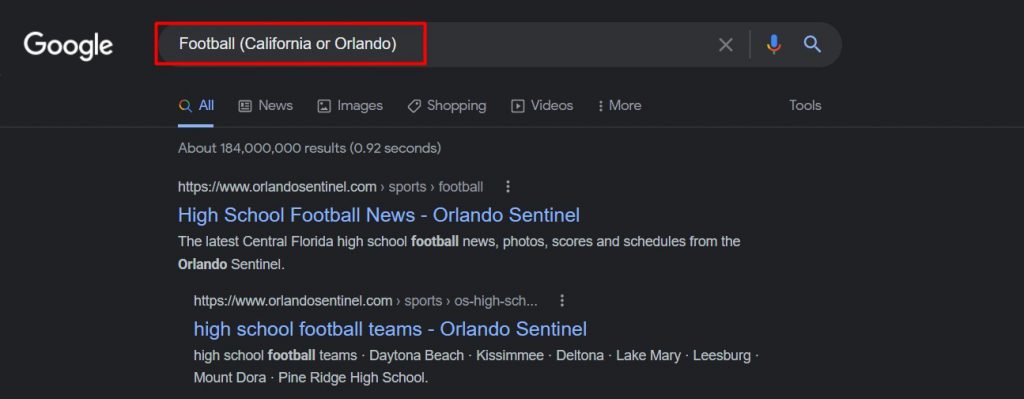
5. Parenthesis ()
Parenthesis is an extension of “Or” Google search operators to combine words with either of the search terms mentioned within the brackets.
Confused?
Let’s simplify this with an example.
For example, say you want to search for Football in California or Orlando. So you’d search for Football (California or Orlando) to get the results related to either “football California” or “football Orlando.”
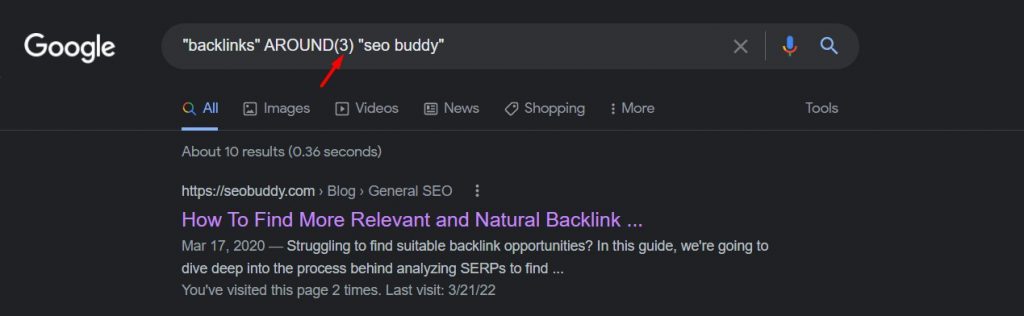
6. AROUND (#)
If you’re searching for keywords that don’t sit together naturally but you want to discover content related to them, you’d use AROUND (#) to narrow down your hunt.
The # is replaced with the number of words you’d want between your keywords. For example, in the next image, we’re using AROUND (2) which means there can be two words between “backlinks” and “SEO Buddy.”
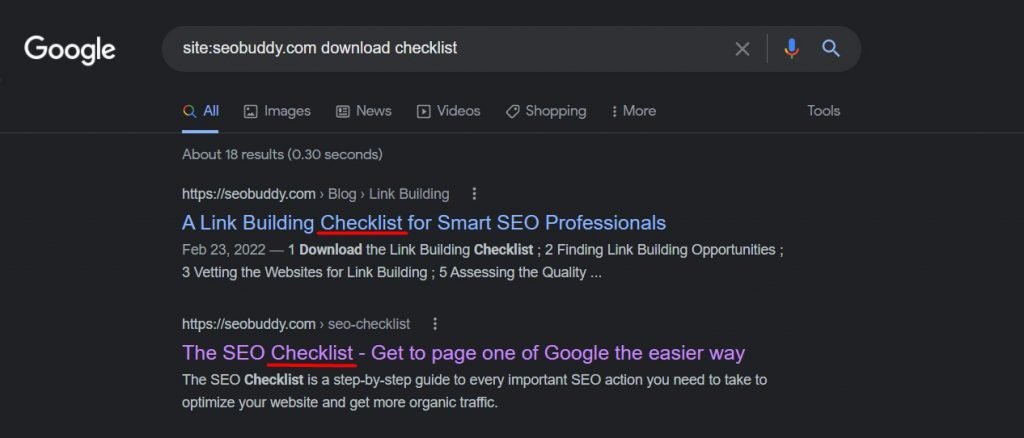
7. site:
When you are looking for web pages or content from a particular website or type of website, you can use the “site:” Google search operator.
The “site:” operator can also be used for several other purposes like finding internal duplicate content, multiple related pages of a website, linking opportunities on a specific site, etc.
Here is what you’d search for if you want to download SEO-related checklists from your favorite SEO tool.
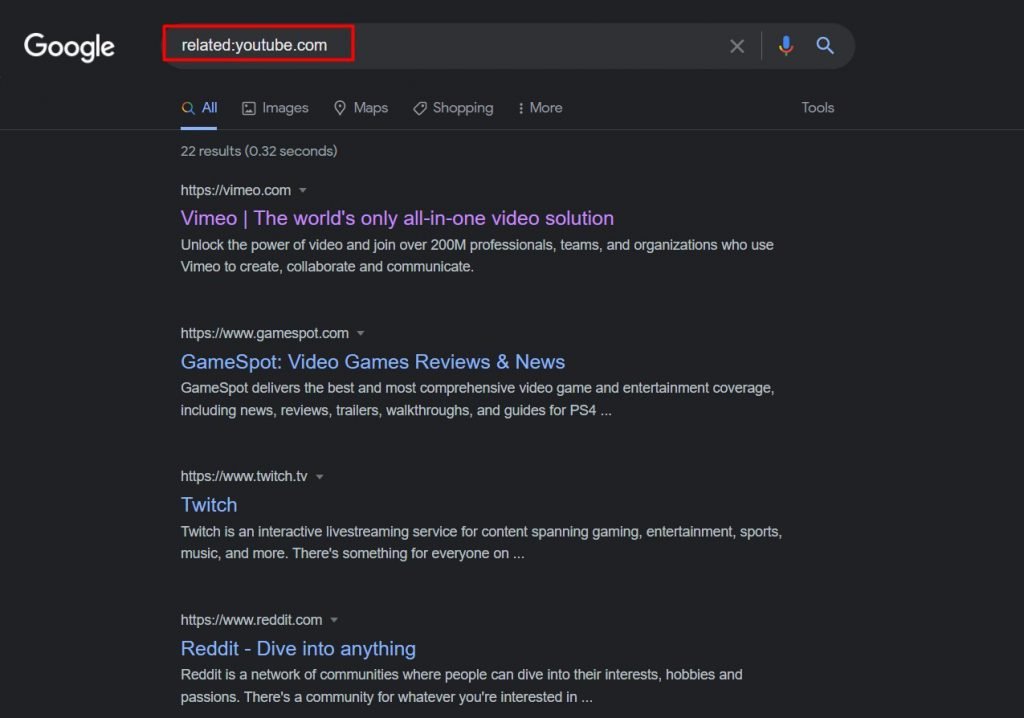
8. related:
We’ve all been there when we’re looking for new sites that have similar content to a site that we know. The “related:” Google search operator does a fantastic job finding such domains and shows a list of similar sites.
Give it a try.
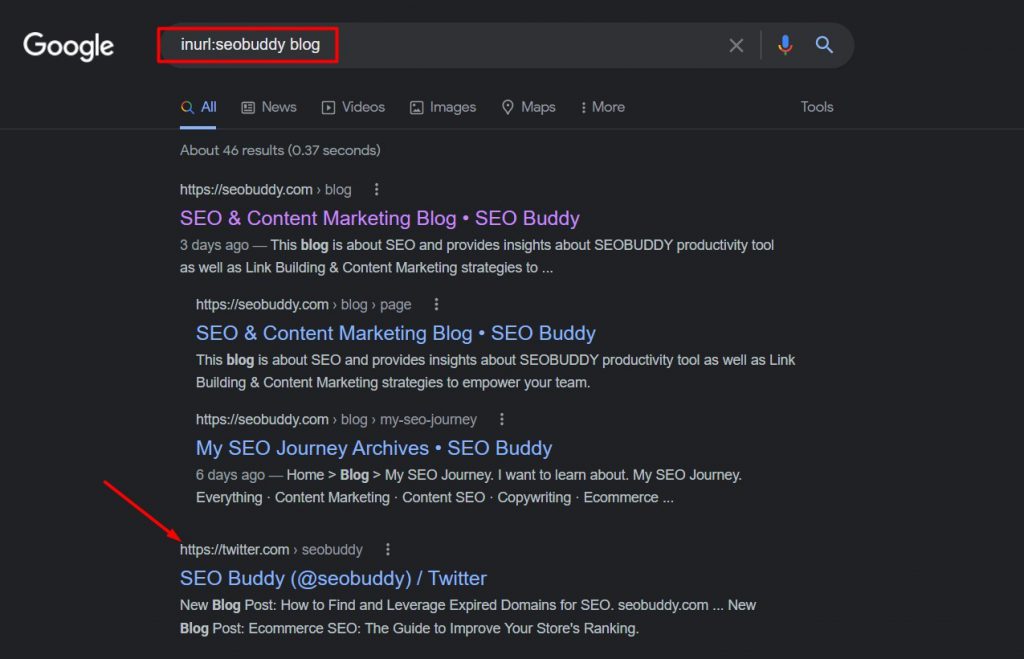
9. inurl: and allinurl:
Both these search operators are helpful in narrowing down the search to only pages with specific text in the URL. “inurl:” is used when you want only one, either of the words, or all of the words in the searched URLs.
Take a look at the following search result where the URL doesn’t necessarily include all the terms specified in the search intent.
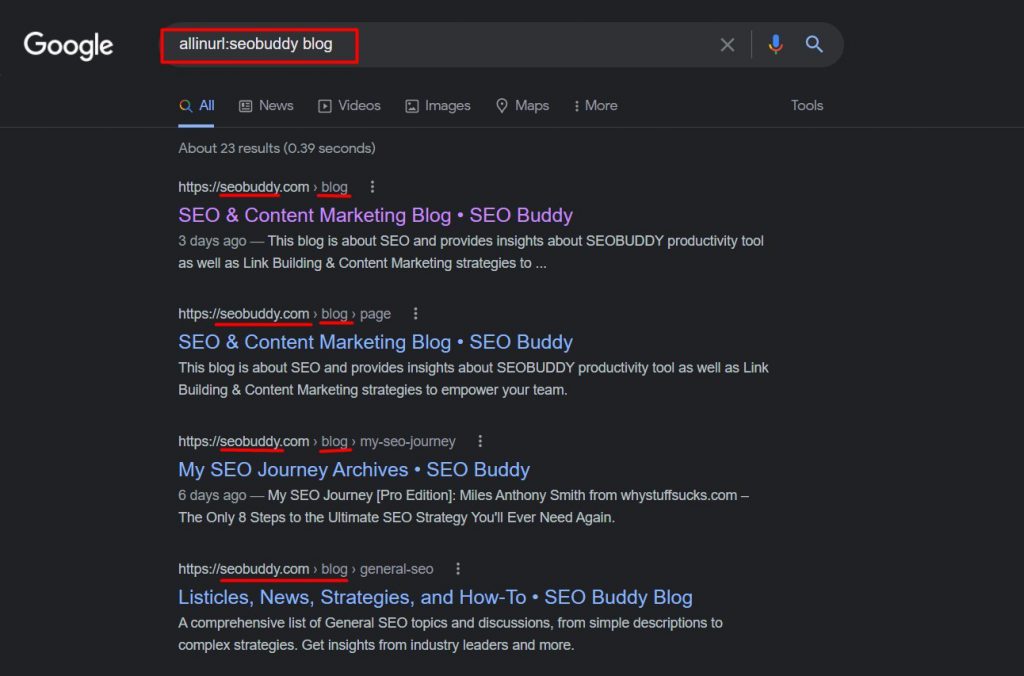
Whereas “allinurl:” is used when you want all the specified words in the URL to show up. Here is an example of how using “allinurl:” will get you to search results that include all the specified words in the URL.
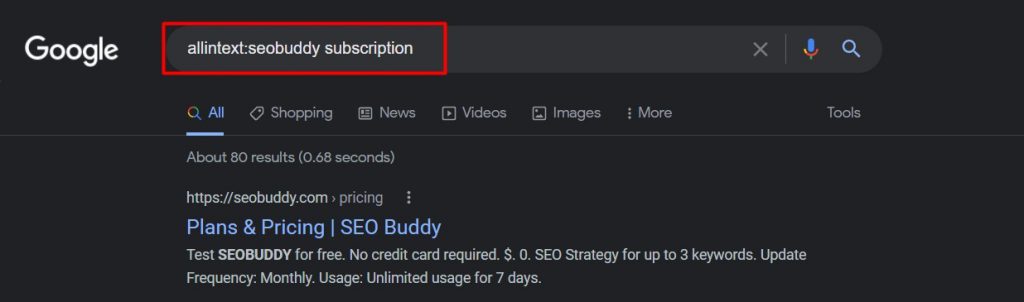
10. intext: and allintext:
This Google search operator is very similar to the previous one — “allinurl:”.
While the intention there was to have the search term in the URL, here the purpose is to ensure the word(s) are included somewhere on the page.
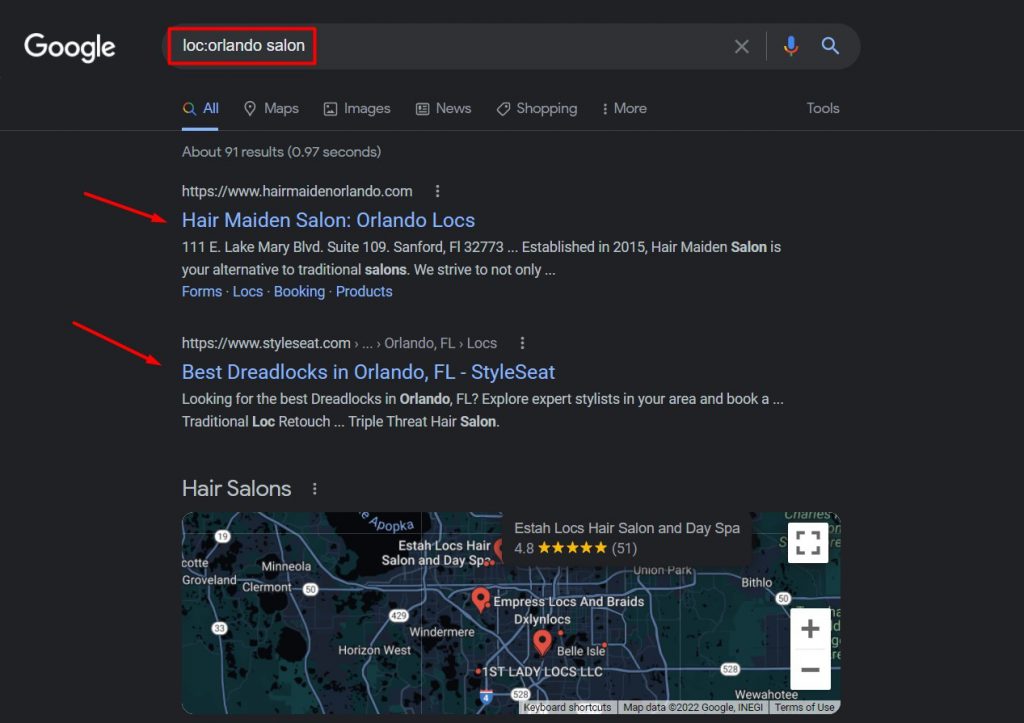
11. loc:placename
Most SEOs work for customers at different places and require specific results from a particular area to analyze the competition, keyword intent, and even the industry standard.
While Google does give you an option to get the results from specific countries, you’d want hyper-personalization in terms of maybe SERP for a city.
This is where this search operator comes in handy. Using it helps you get location-specific results.
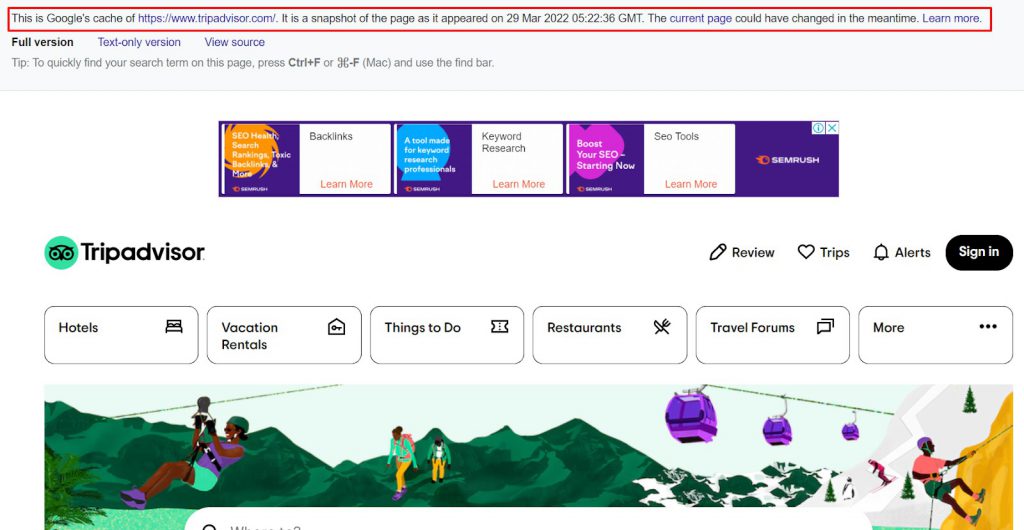
12. Cache:
Mythbuster – It’s not an operator that gets you search results; still, it’s useful in several aspects.
Using the “cache:” search term, you can access the most recently cached version of any webpage.
Let’s assume that a site is down, but if you want to access its most recent version, you’d put the following in the URL box – cache:website.com.
You can even use this search term to check when a particular page of your website was cached. Here are the results you’d get when you make this query.
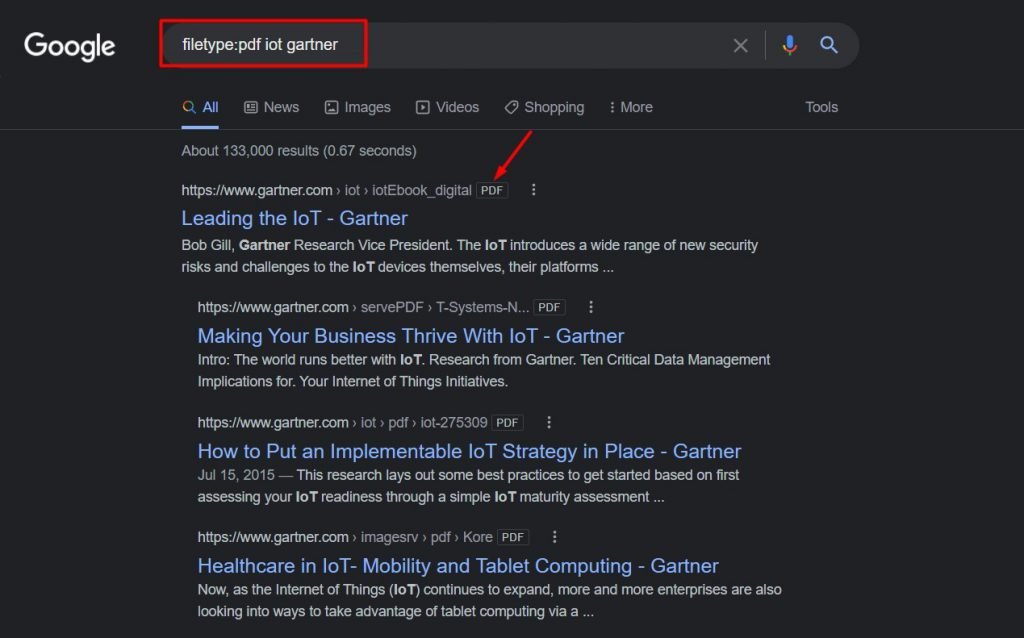
13. filetype:
If you’re looking for specific types of files in the Google SERP, this search term is the best option for you.
Simply search for filetype:yourfiletype keyword, and the SERP will show the most relevant results to you.
Google Search Operators That Somewhat Work
Here are some Google search operators that don’t work with complete effectiveness now. Yet, they’re great to have as you could still filter out some of your search results with them.
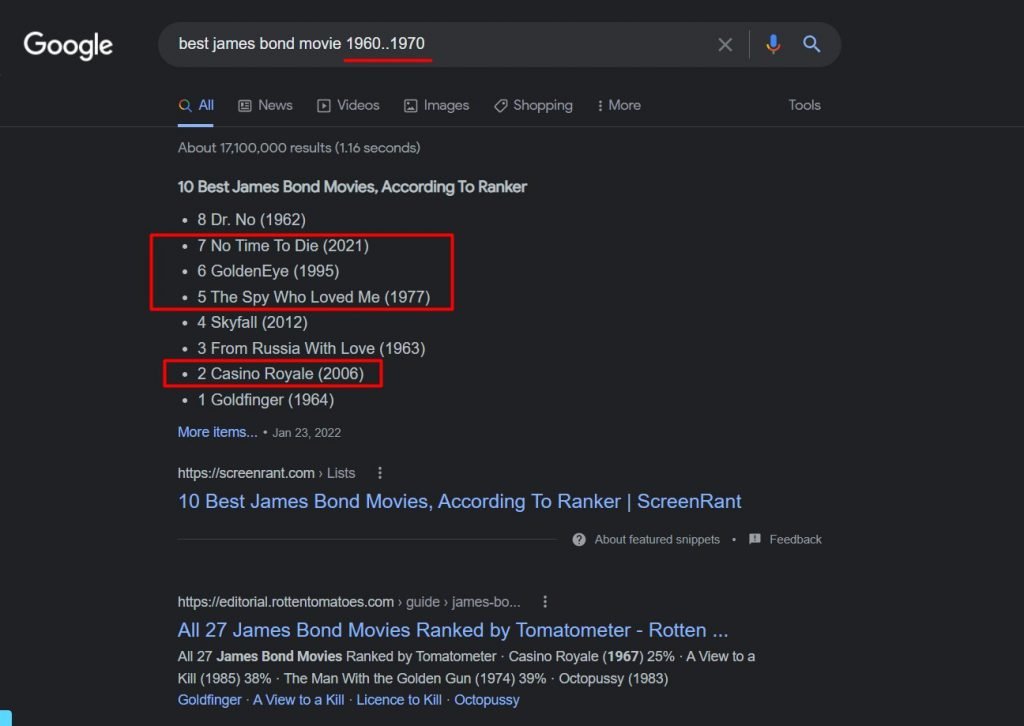
1. Year..Year
If you put two dots between two years, the Google SERP will only include pages that fall within your range.
Although this search term does help you get the desired results, the caveat here is its inconsistency.
To test if this search term still works, we tried finding James bond movies between 1960 and 1970, and the results were somewhat disappointing.
To be frank, you cannot expect this operator to provide you with the results of a time frame only. Still, it’s effective in narrowing down your search to some extent.
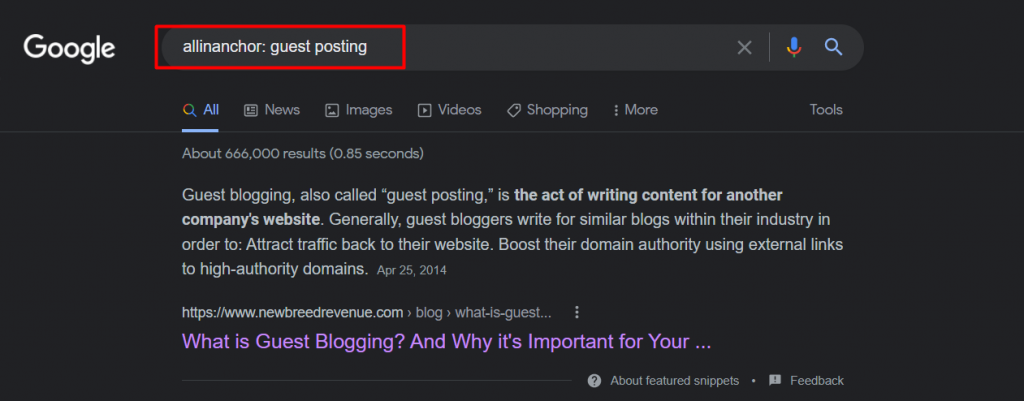
2. inanchor: and allinanchor:
This Google search operator used to come in very handy while looking for pages that are linked using specific anchor text. When we tried them while writing this article, they didn’t seem to work most of the time.
Here, take a look at a simple search we tried for allinanchor: guest posting, and the results didn’t have any link (at least on the top) which had the same term as an anchor. That said, it did bring up a relevant result about “guest blogging” instead.
3. blogurl:
As Google blog search was discontinued way back in 2011, search operators related to Google blog search either don’t work anymore or aren’t accurate. In addition to “blogurl”, the following search operators aren’t that active now:
- inpostauthor:
- allinpostauthor:
- inposttitle:
You could, however, try them to see if they work for you.
4. link:
This search operator was used for finding pages linking to a specific URL or domain. Although Google discontinued this operator in 2017, it does get some relevant information, if not accurate. You could still use it to filter out irrelevant search results.
5. info:
This operator is used for finding information about specific pages, including similar pages and recently cached pages. The search operator “id:” could also be used in place of this, and the results would be similar.
Although the “info:” search operator is dead in the current scenario, it can still be used to find the canonical and indexed versions of a URL.
How SEOs Can Use Google Search Operators
Now, we’ve covered most of the functional Google search operators. It’s thus time to understand how we can use them for our SEO efforts.
Let’s go through Google search operators’ use cases one by one.
1. Find Internal Linking Opportunities
Internal linking is crucial for every successful SEO strategy. However, finding new opportunities within a website consumes time.
It’s hard to know which blogs/web pages have a specific keyword you’re after, especially when you have hundreds of blogs on your website.
You can speed up your hunt for new internal linking opportunities by using a combination of advanced Google search operators.
For instance, let’s assume that you have written a blog post related to “content,” and you want to interlink this post with a few other related posts on your domain. Here is how you can find the opportunities via Google search.
Use the “site:” search operator to define your domain, use “-site:” to exclude the new blog you want internal links for, and use “intext:” for the keyword(s) you’re after.
For this illustration, we’re using:
- site:seobuddy.com
- -site:seobuddy.com/blog/how-to-write-great-content-that-ranks/
- intext:content
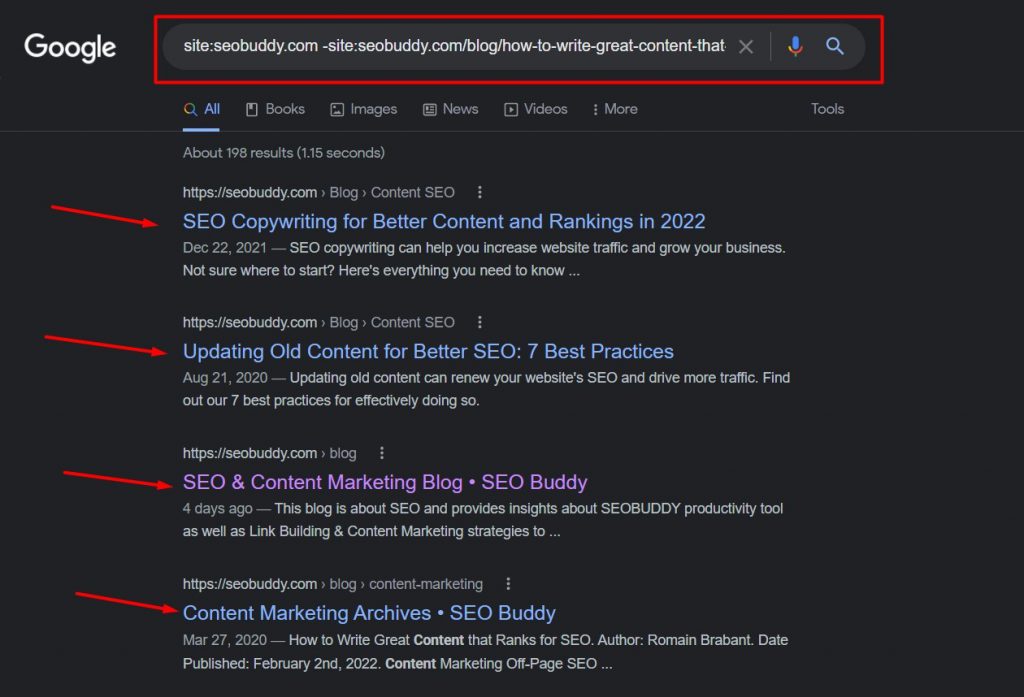
See, tons of new internal linking opportunities. Just open the URLs and find the perfect place to link back to your new blog. Easy peasy.
2. Analyze the Topics Your Competitor is Writing About
Keeping an eye over competitors is an essential part of any SEO strategy. You must know what they’re posting and what’s working for them to understand their strategy.
However, manually scrolling through your competitors’ websites isn’t the best approach for competitor analysis. Instead, you can make use of Google search operators to speed up the process.
Here is how to do it.
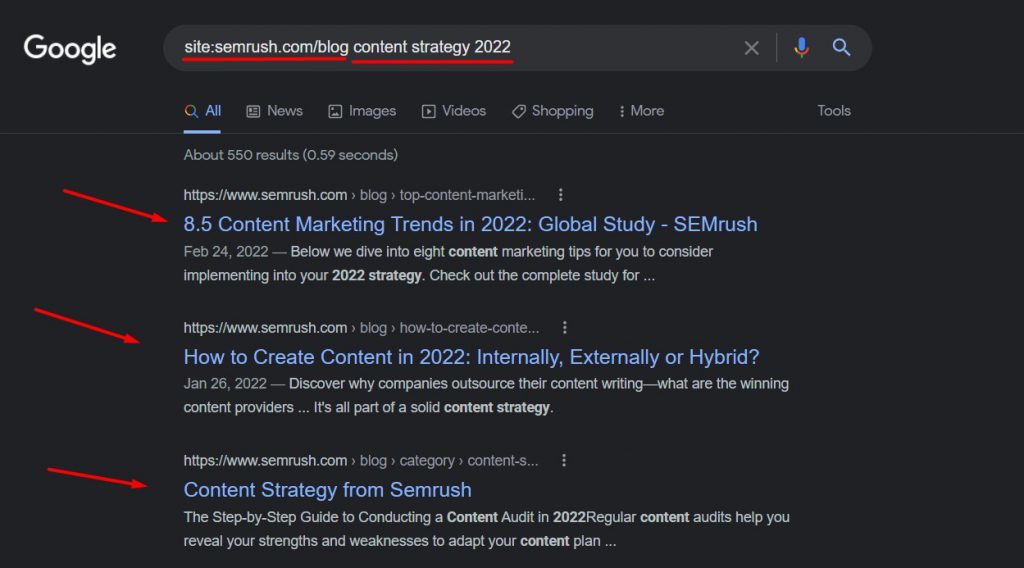
Let’s assume your SEO analyst wants to analyze the specific content of one of your competitors. They could search for site:competitordomainname.com/blog keyword or topic.
If they want to search for a particular phrase instead of a keyword and want to get the exact match search results, they can add quotes (“”), but for general subjects, without quotes is fine.
3. Find Guest Posting Opportunities
Finding new guest posting opportunities is always cumbersome and requires significant time and effort from SEOs.
Thankfully, you can use a combination of search operators to speed up your hunt for new domains for guest posting.
Here is how to do it.
Search using Google search command keyword intitle:”write for us” inurl:”write-for-us”
As an example, here is what the search operators look like in a hunt for EdTech guest posting.
Here, we’ve used three search operators to narrow down the search for the most relevant domains.
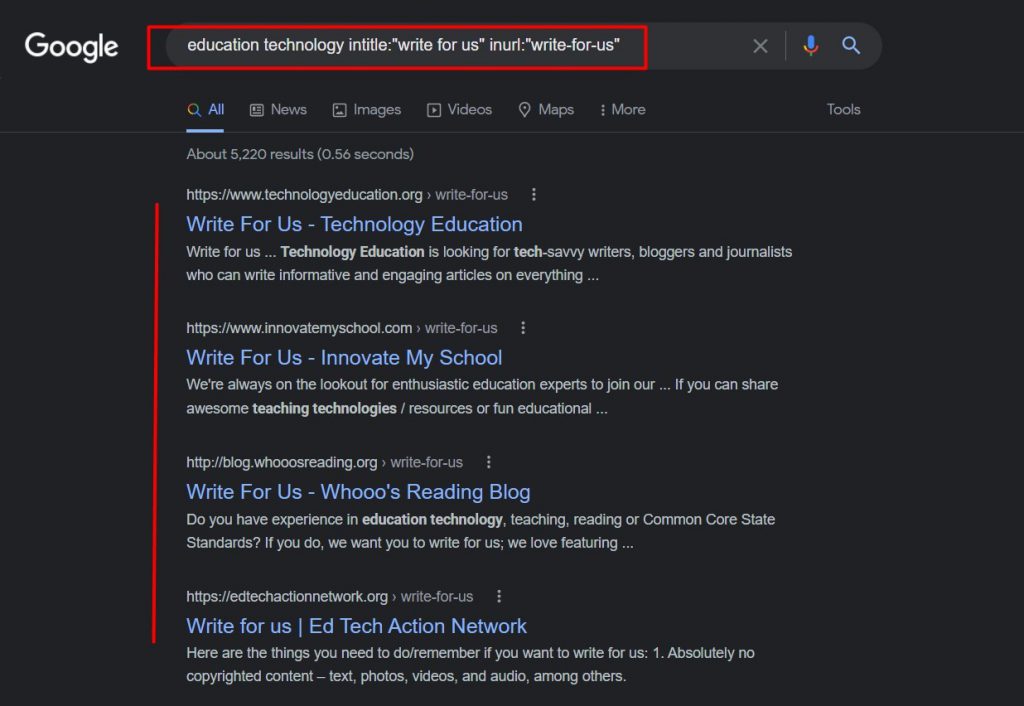
However, if you don’t find many domains via this search, try changing the keyword phrase with “become a contributor”, “guest post guidelines”, etc.
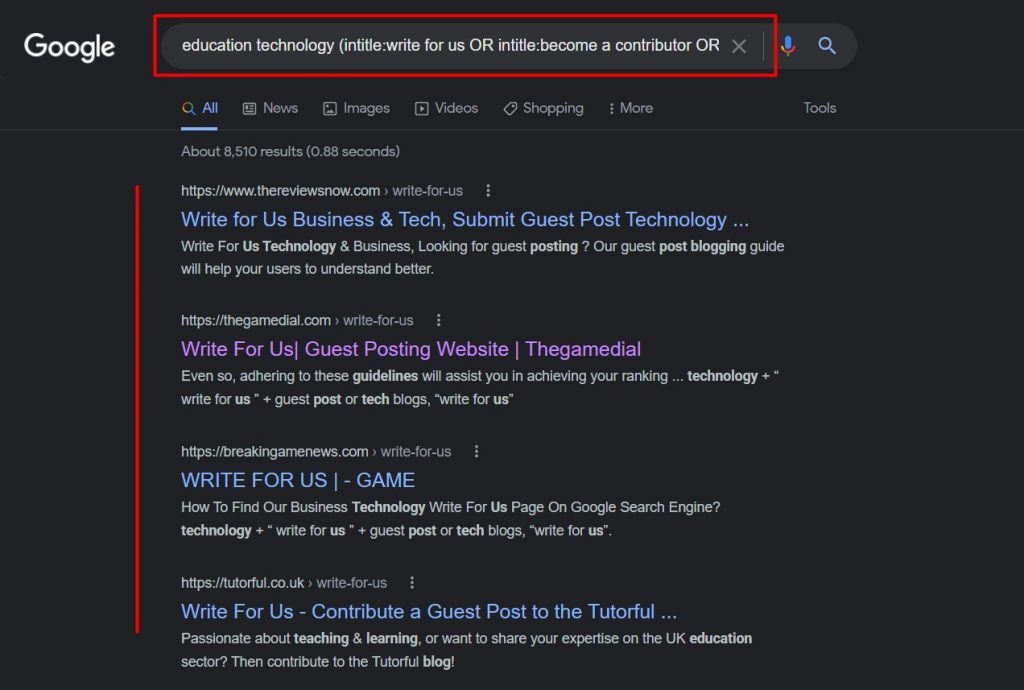
You can also try broadening your hunting area by using the following Google search command:
keyword (intitle:write for us OR intitle:become a contributor OR intitle:guest post guidelines OR inurl:guest-post)
4. Find Opportunities for Backlinking
If you’re looking for new backlinking opportunities that might accept your link in the resources section, a combination of search operators can come in very handy.
Here is a mix of search operators you should try for broader Google search commands. This particular example is in relation to edtech firms so we’re searching for edtech resources using the following command.
EdTech(intitle:resource OR intitle:resources OR inurl:resources)
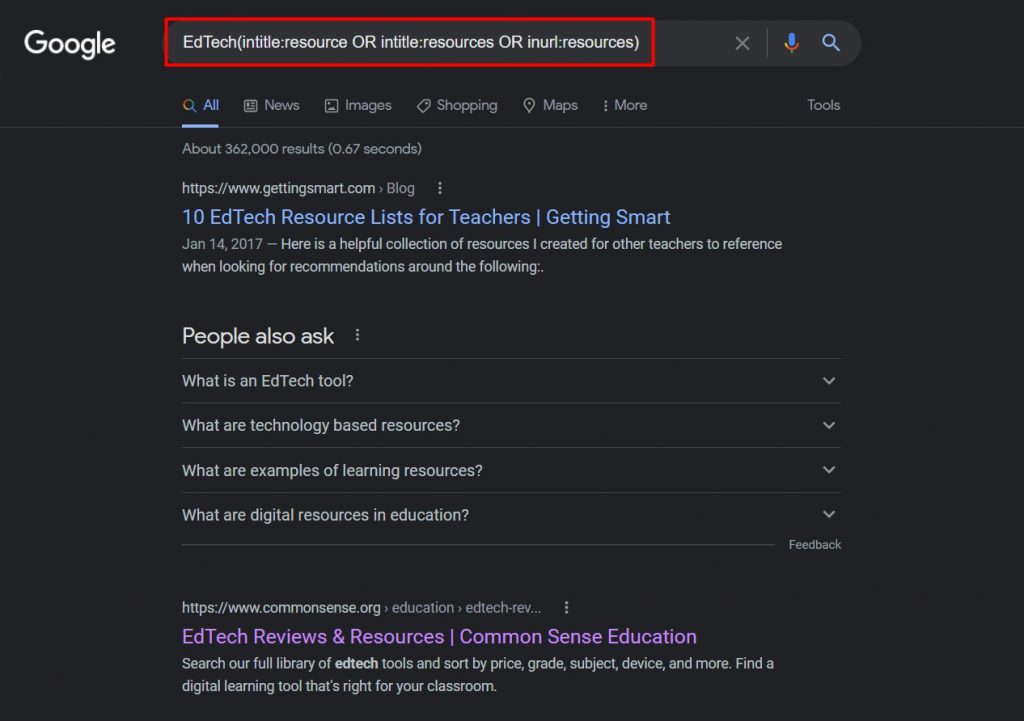
If the results you get from these search operators are broad, you can try to narrow them down by using a variation of search operators like the following:
intitle:EdTech resource OR intitle:EdTech resources OR inurl:resources
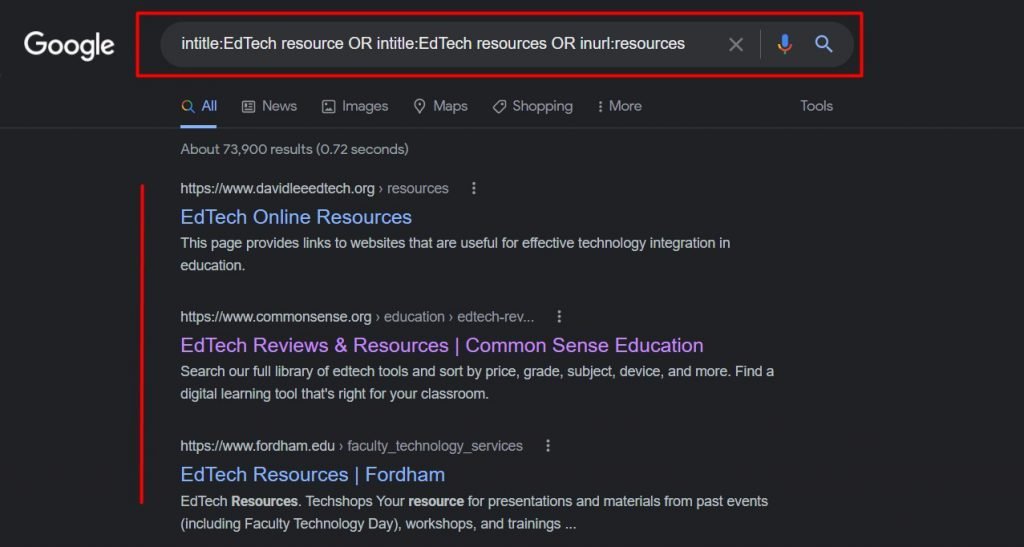
As you can see, with a slight change in the search operators how easily we could find more relevant results.
5. Discover Infographic Posting Opportunities
Infographics are a great way to build backlinks if you know how to leverage them. Additionally, their engaging nature makes them great for spreading brand awareness too with off-page SEO.
However, one constraint many SEOs face is not finding many infographic submission sites.
Even a simple Google search query like “infographics keyword” would be sufficient in the early stages of your SEO.
Still, you need to find new Google search commands as you might already have created backlinks from those domains.
This is where Google search operators can be useful for you. Try using variations of your keywords in the following mix of advanced search operators:
“keyword” intitle:submit an infographic inurl:infographic
Check the following screenshot of how you could find relevant domains that accept infographics on education.
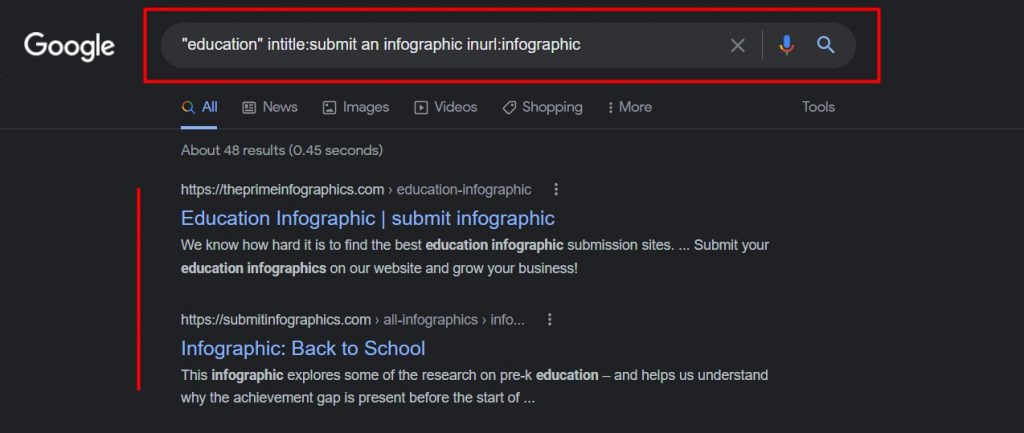
6. Find Journalists or Contributors for Your Blog
It isn’t always possible to guest post on several popular websites like Entrepreneur, Forbes, etc. for backlinks due to difficulty in getting a guest blogger status on them.
However, you could partner with existing contributors and authors on these domains to get backlinks and mentions.
But how do you find these contributors?
Don’t worry. Advanced search operators can help you with this as well.
Using them, you can easily narrow down your search and spot potential contributors for your guest posts.
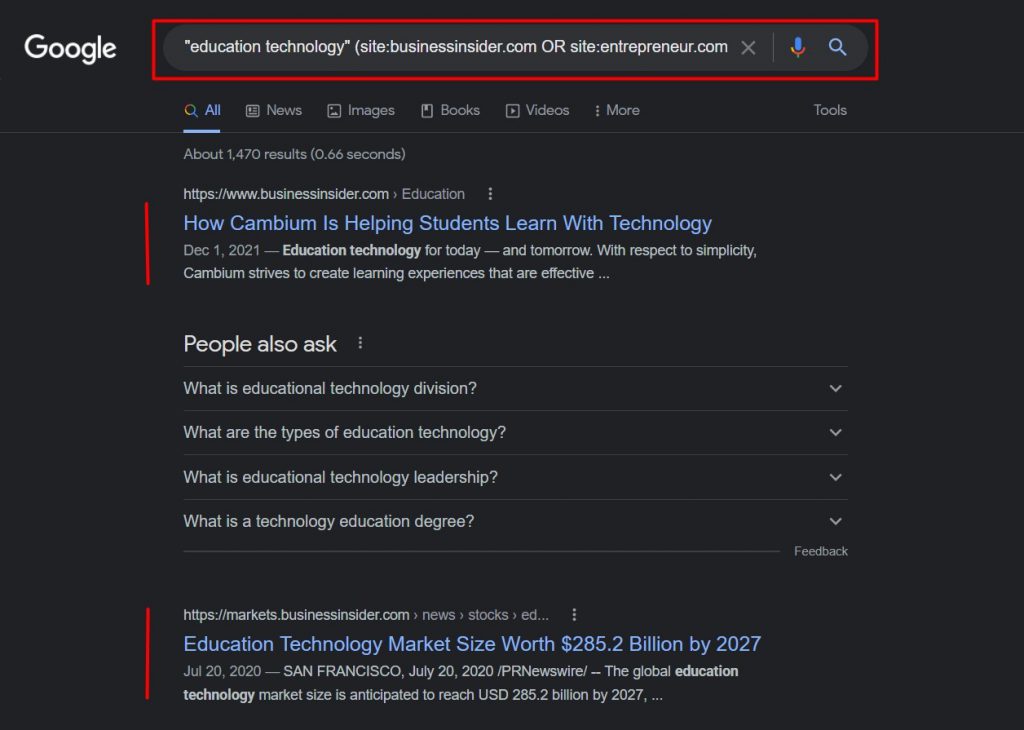
You can simply search using the following mix of Google’s search operators to get the desired search results for contributors:
- site:domainname.com keyword
- site:domainname.com keyword “name of the author”
- author name (site:domainname.com OR site:domainname.com OR site:domainname.com)
These mixes of advanced search commands work most of the time. Here is an example of finding blogs related to your keyword in several domains. You can then open these links and decide whether you’d like to reach out to the contributor for a collaboration.
7. Find Competitor Mentions to Identify Opportunities for You
The best part about this method is you don’t need any tool at all. By just searching using an advanced search command on Google search, you can find tons of insights into your competitor mentions.
Isn’t it cool?
Here’s a simple mix of search commands you can use to find your competitor’s mentions online:
intext:”competitor’s brand name” -site:competitorsite.com
This mix should get you loads of domains where you can also try to get mentions or other types of backlinks.
You can broaden your search for competitor mentions by including several competitors in the mix. You could accomplish this by using the OR operator.
Here is how it looks:
(intext:competitor 1 OR intext:competitor 2 OR intext:competitor 3) -site:competitor1site.com – site:competitor2site.com -site:competitor3site.com
Let’s try this.
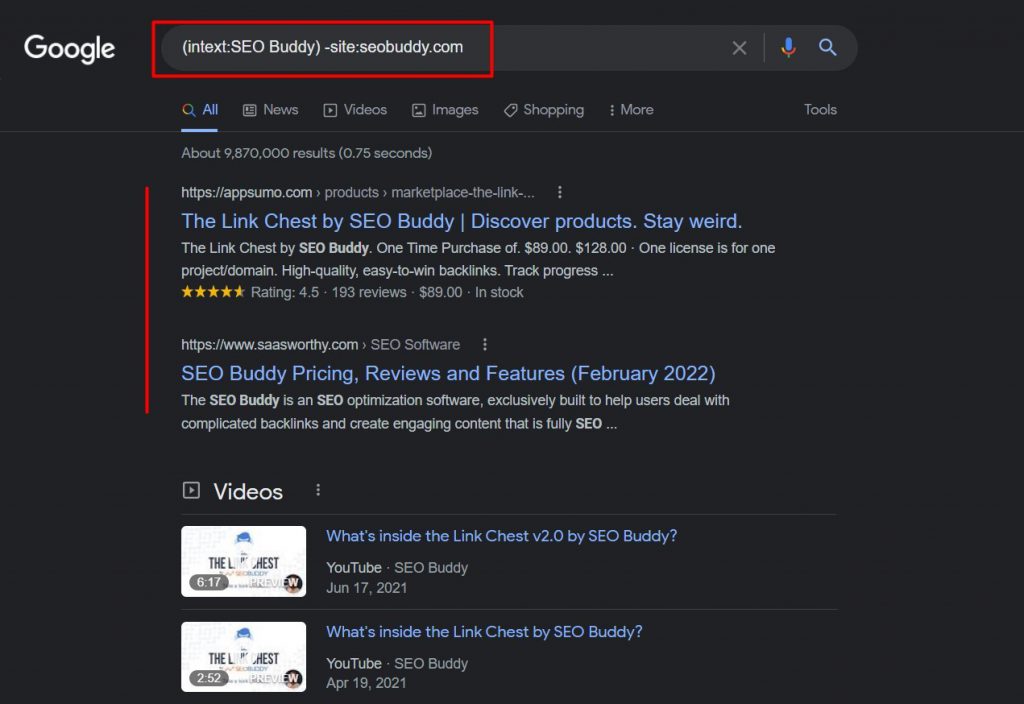
This works flawlessly. Note how you can easily see every single website where the brand has been mentioned. You could even use this to find your own brand mentions online like we’ve done above.
8. Find Non-HTTPS Indexed Pages of Your Domain
Having a secure website is not an option these days. It’s critical for improving your SEO. Hence, it’s essential for SEOs to keep a check on non-HTTPS pages on their domain.
While you can find non-HTTPS URLs during technical SEO audits, here’s how you can find them without investing in any costly SEO analysis tool.
All you have to do is search for site:yourdomain.com -inurl:https
Doing this will bring up a list of all the URLs that are non-HTTPS on your website.
Let’s try this with our own website.
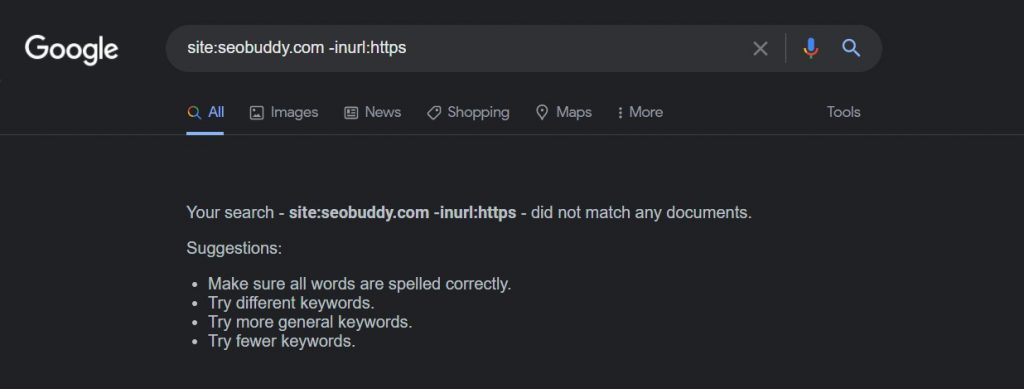
It looks like SEO Buddy doesn’t have any non-secure URLs.
You better try this quick technique during your own website’s technical SEO audits and if you find the non-HTTPS pages, check your SSL certificate to see if it’s valid. You could also see if you need to do a 301 redirect on the page.
Take a look at Apple’s domain having not-secure URLs.
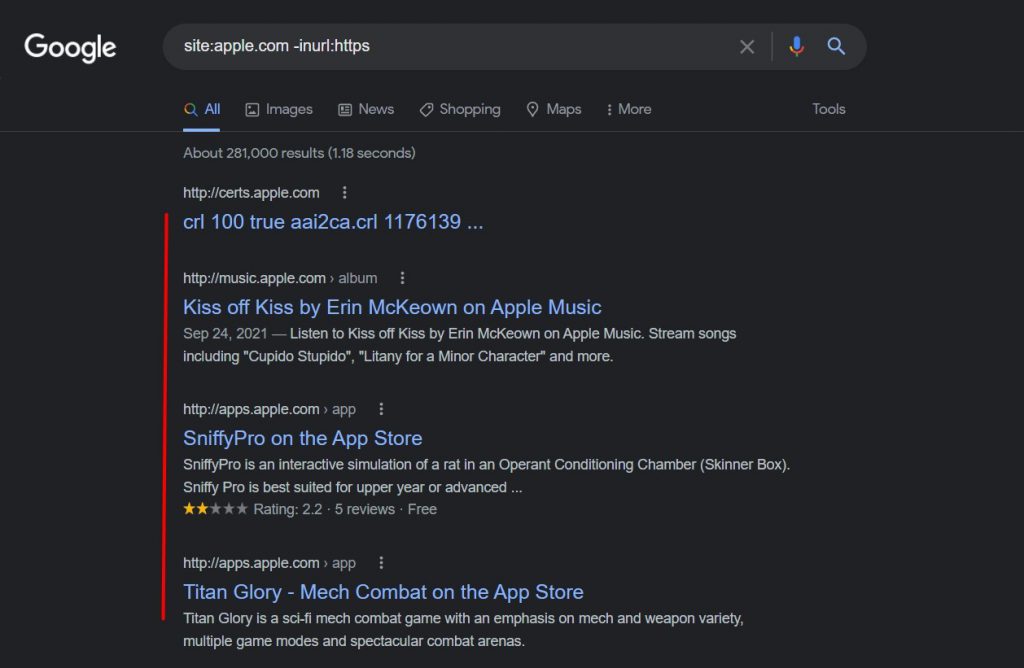
9. Find Statistics and Research Related to Your Content
Content writers often face challenges while searching for the latest case studies and research to back their claims.
A simple search on Google like mobile phone user demographics statista won’t surely get you trusted research. This can lead to endless scrolling and search cycles.
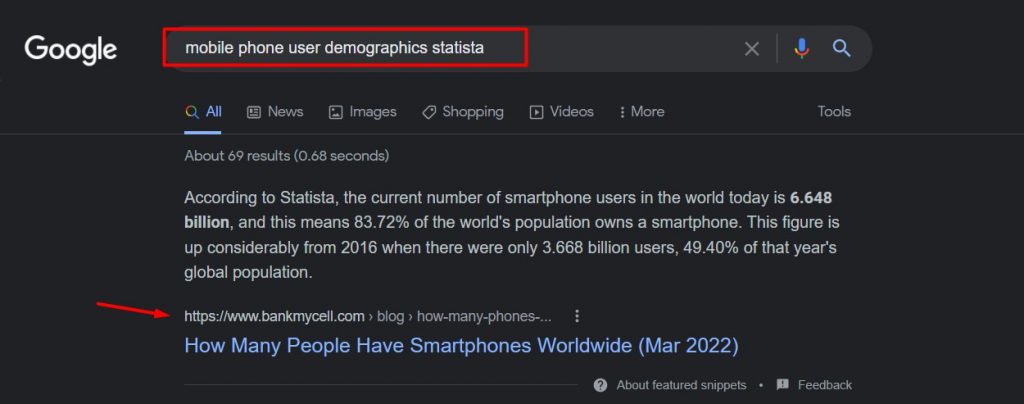
You can easily see that the first search result is an answer box, which isn’t a credible source.
This poses a problem as you won’t be well-positioned to find the right sources for your content. Additionally, it’d lead to a lot of time being wasted in the process.
That’s where search operators can help.
If you try a mix of operators in the Google search box, you will surely land on the correct research report.
Here we tried testing its effectiveness.
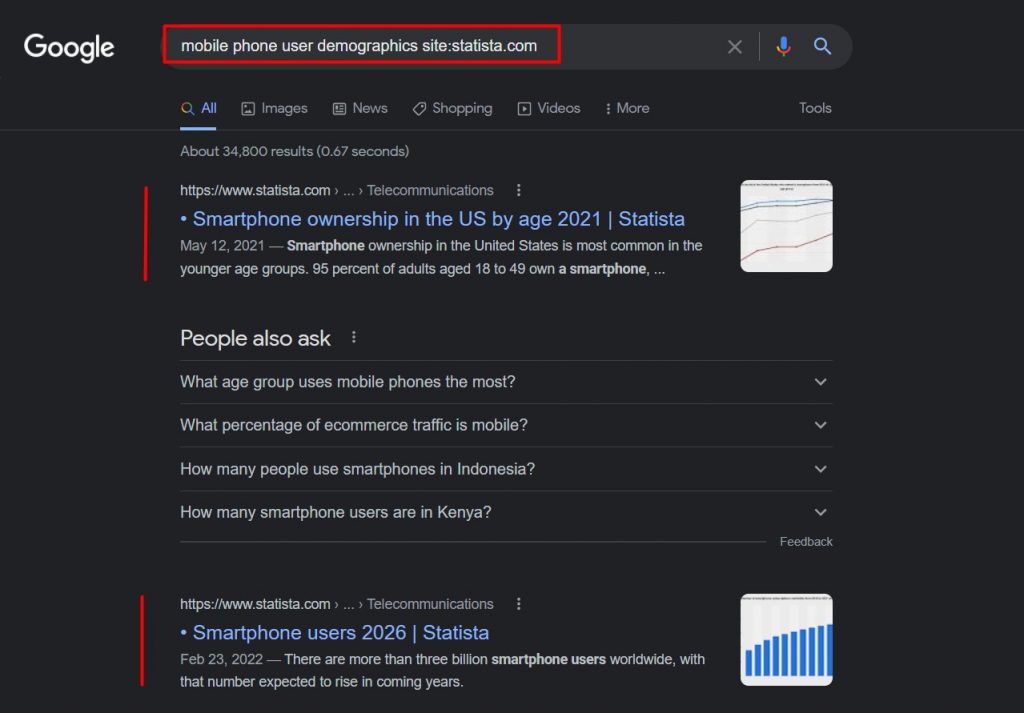
By simply putting the site: operator, we could populate our SERP with the most relevant studies from Statista.
10. Find Q&A Threads Related to Your Keyword
SEOs love platforms like Quora, Reddit, etc., which have relevant threads and are easy to publish content on. Although these links are no-follow, forums aren’t about building links; they’re about public relations and building your authority.
But how do you find relevant content on these platforms?
Thankfully, the process is simple with search operators.
You can try the following mix of advanced search commands on Google:
site:sitename.com (intitle:keyword 1 OR intitle:keyword 2 OR intitle:keyword 3)
We tried this to find threads related to SEO on Quora, and you can see the top results in the following screenshot.
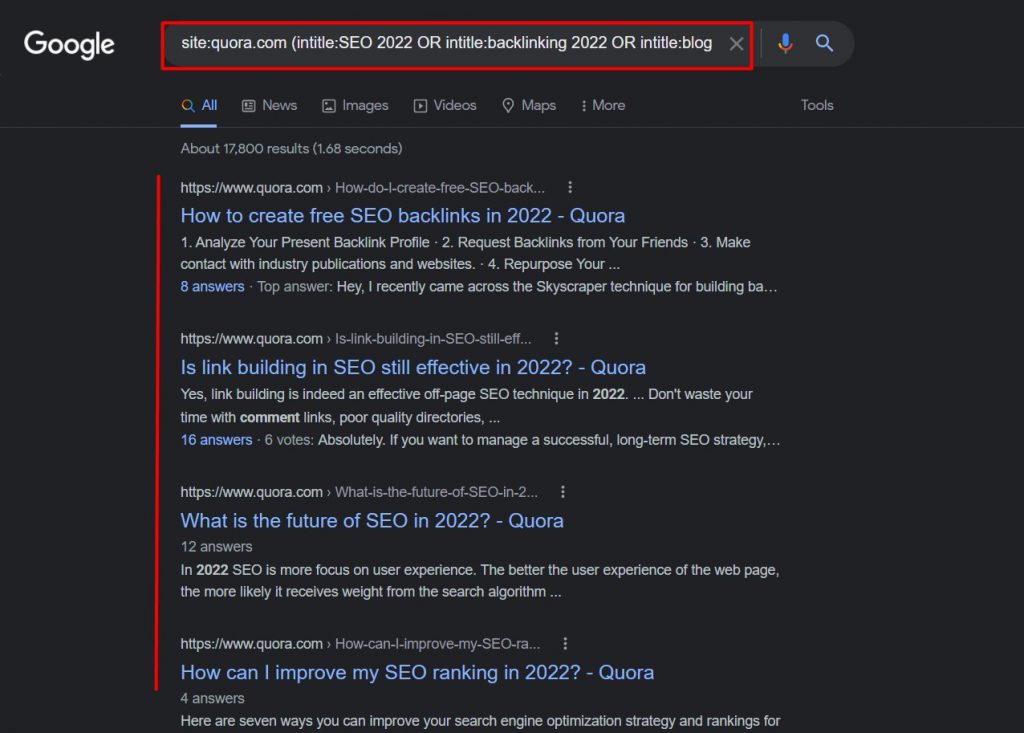
With this simple mix of search commands, you can easily find numerous opportunities where you could answer questions and showcase your authority to your audience.
Why limit this only to Quora?
Let’s go wild and try another mix of search operators.
This time, we’ll query the Google search to include several forums like Google and Warrior Forum in the URL, and the title command will remain the same as the previous one.
Note how it brings up content related to both the forums here.
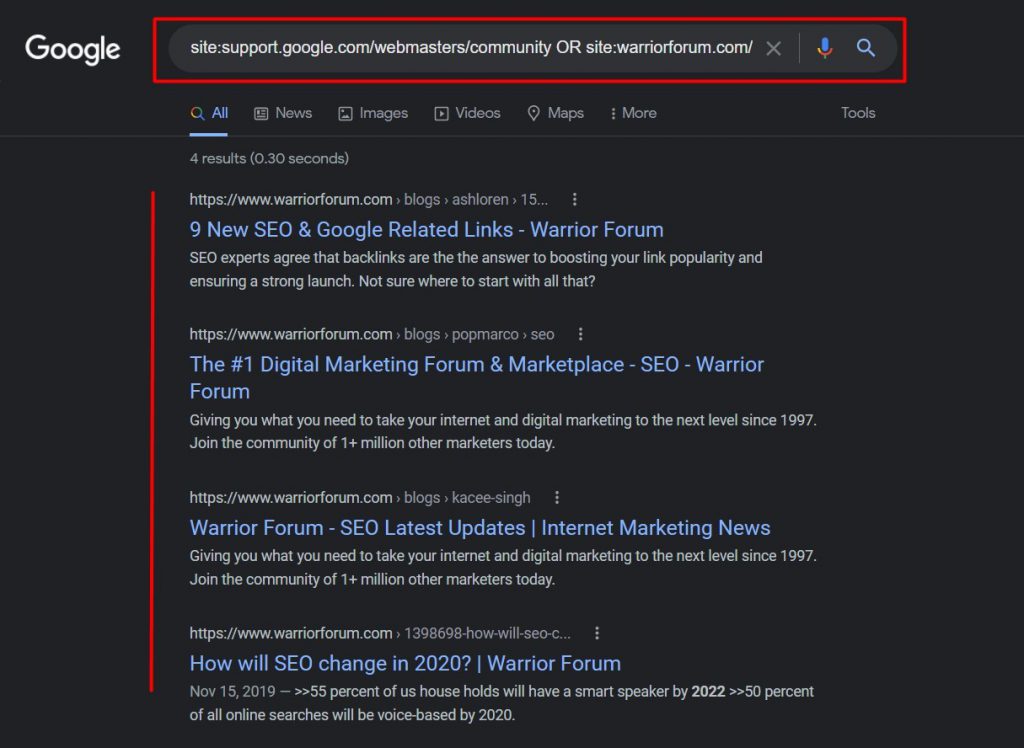
To be frank, this works like a charm. Give this trick a try. It’s very handy.
FAQs
1. What are the Google search operators?
Google search operators are a combination of words and symbols that help Google improve the search engine results. The search operators allow you to command Google about what it needs to include in the SERP and what to exclude.
One such example of a basic search operator is the quotes (“”). If you quote a search query (like “blog commenting is dead”), your Google searches will include only those URLs that have the exact match of the text you’ve searched for.
2. How do I use Google search operators?
You can either use a single Google search operator or mix up some search operators to further enhance your search results. You can use the search operators just like you search on Google in the search box.
For example, you can use the basic Google search operators like “AND or OR” to personalize the search results as per your need along with your search query.
3. What are search operators’ use cases with examples?
You can use Google search operators for specific purposes like:
- Find internal linking opportunities
- Analyze the topics your competitor is writing about
- Find new guest posting opportunities
- Find resource opportunities for backlinking
- Discover infographic posting opportunities
- Find journalists or contributors to a blog or website
- Find competitor mentions to identify opportunities for you
- Find non-HTTPS indexed pages of your domain
- Find statistics and research related to your content
- Find Q&A threads related to your keyword
4. What are Boolean search operators?
Boolean search is named after the work of British mathematician George Boole. In the theory of mathematics by George Boole, all the variables are either “true” or “false.”
The Boolean theory uses three main operators (AND, OR, and NOT) to organize and deliver relevant results to the users for the Google search.
There are only five elements of syntax in the Boolean search operators:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- ()
- “”
5. How do I use Google advanced search operators?
Using Google search operators is very easy. You just have to:
- Think of a goal behind your Google search.
- Identify the search operators you’d have to use for the particular search.
- Create a mix of search operators.
- And press enter.
If you aren’t sure where to start, scroll up to the previous sections where we’ve discussed how to use search operators for SEO.

Now it’s time to discover the other 102 steps that will get more organic traffic flowing to your website. Get the SEO Checklist here.
Want to get a sneak peek of what it looks like?
Enter your email and get a free demo version of the SEO Checklist.
Wrapping Up
So far, we’ve seen that Google search operators are indeed the best free technique for performing several SEO activities, including competitor analysis and backlinking.
While using the search operators individually is great, you can further amplify their effectiveness by using multiple search operators together.
But there’s a problem.
As there are dozens of search operators you can choose from, it can be challenging to remember it all. Add to that the fact that there are several ways you can mix them to find useful insights for your SEO, and it can be quite a difficult task.
In such a situation, it helps to have a handy resource to refer to for simplifying your Google searches.
Hence, we’ve created a list of Google search operators that you can download for offline use. Download it here.





Thank you so much, It is really amazing SEO content you had made. It really helpful for me.