Google Cache Search: How to View Cached Pages and Websites
What’s the simplest way to check how Google is indexing your content? How can you view content on web pages with a 404 error or check when web pages were last indexed by Google?
The answer is simple. You can use Google cache search.
Of course, you can extract all this information from your Google Search Console, but the Google cache search tool offers the simplest method.
Read on to learn more about Google cache search, the importance of Google cache, and how to view cached pages.

What is Google Cache?
As a website owner, you always strive to make your website discoverable by your target audience.
To achieve that, you create relevant content that’s optimized with the keywords your audiences search for on Google, use beautiful images, share informative content, etc.
All this helps Google crawlers to understand your content well and rank your website.
When the crawlers index your website, they create a backup of the web pages and store it in a Google Cache.
This is to help users view older versions of a website, especially during downtime or when your website is not loading properly. Google also uses the cached version of a website to deliver search results.
Note that not all pages are indexed by Google.
Google cache search can help you see cached pages, which allows you to see what pages aren’t indexed.
This tool also helps you to check the date and time when Google cached a page you recently updated, or discover old content.
What’s more?
By viewing the content in the Google web cache you can solve technical issues, which can greatly improve your search engine optimization efforts.
Simply, Cache is an internet archive that contains copies of the web pages that are temporarily stored by Google.
Understanding Google Cached Pages
When you view Google cache search results, you will see a banner at the top of the cached page with the following information:
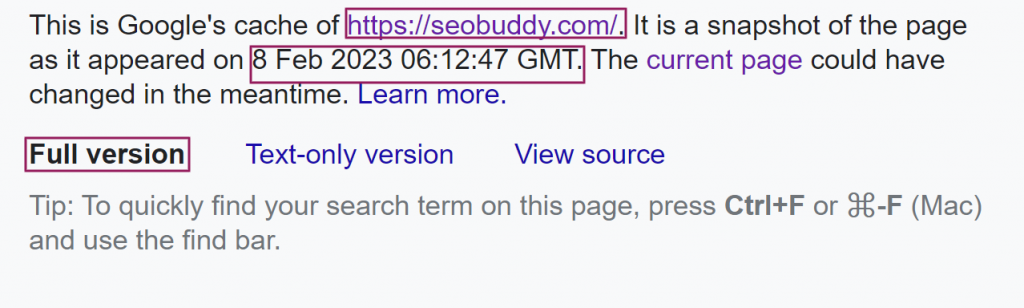
Image via SEO Buddy
- The cached link: This is the URL of the web page you wanted to visit.
- Date and time: This area shows the exact date and time the cached version of the web page was backed up.
- Full version: The full version shows the page you want to visit as rendered by your browser and not Google.
You can also view the text-only version (with CSS turned off and without images) of the page you intend to visit or its source code.
The cached URL in the address bar will look something like this: http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:bViefxhTSpAJ:https://seobuddy.com/&hl=en&gl=ke&strip=0&vwsrc=0
How to View Google Cache Results
There are multiple ways you can view cached pages or cached versions of your website.
In this section, we’ll discuss seven handy ways to view the content of a cached page.
The good news?
You don’t need any technical skills to use Google cache search.
Let’s get started.
1. Find Cached Pages from Google Search Results Page
Here is a step-by-step process to view a web page cached by Google:
- Go to Google.com and enter the URL or keyword related to the content of the page in the search box and hit enter. Then, click on the three dots menu in the result entry that you want.
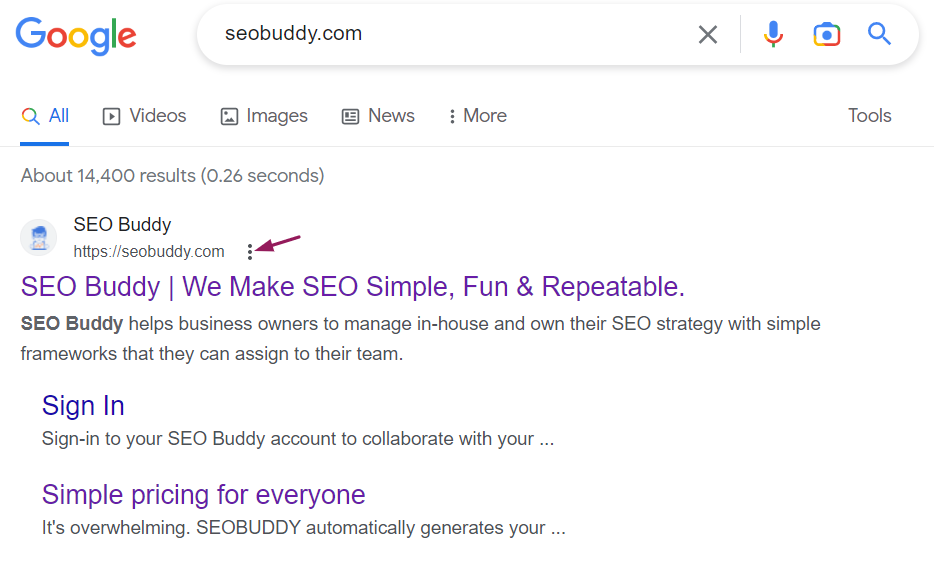
Image via SEO Buddy
- Google will open a pop-up window on the right-hand side titled “About this result.” Click “Cached” to view the cached version of the web page you want to visit.
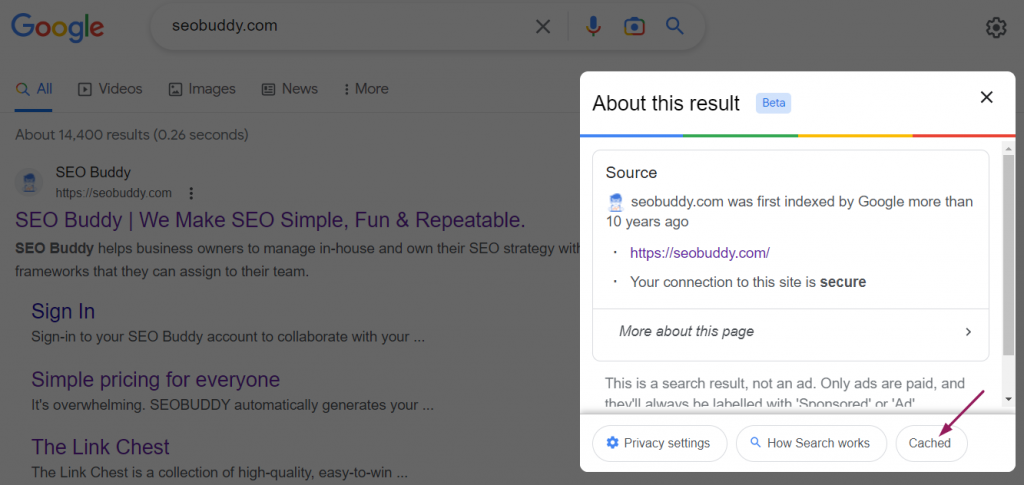
Image via SEO Buddy
This will take you to the cached version of the website/page as shown below:
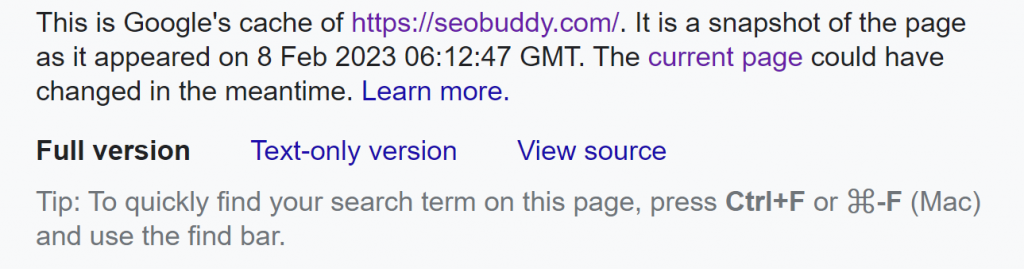
Image via SEO Buddy
From here, you can go to the text-only version of the website, view source, or click the URL to view the full version of the website.
Sometimes Google might not display the cached link if the site owner has instructed the search engine not to cache their websites.
2. Use Google Cache Search Operator
Enter the “cache:” search operator in the search bar to view Google cached results. Follow these simple steps:
- Go to Google.com or Chrome search bar and type cache followed by a colon, plus the URL you want to view its cached version without spacing the words.
Something like this cache:seobuddy.com
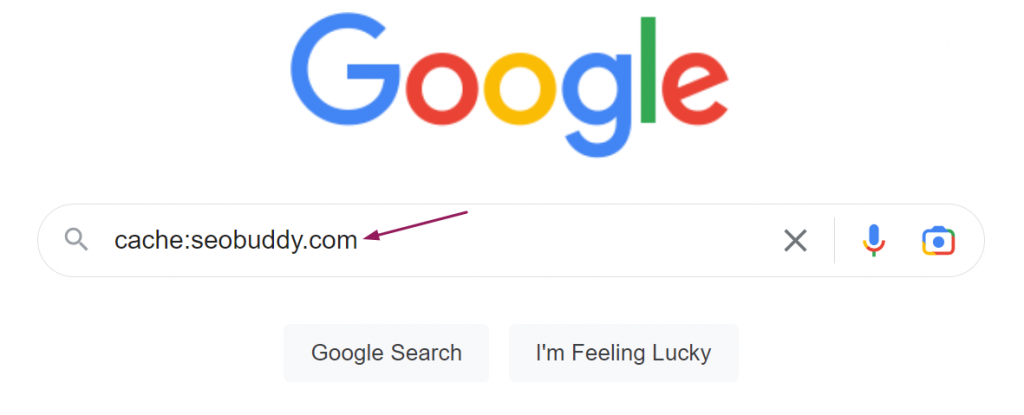
Image via Google
- When you hit enter, you will see the cached page.
3. Use Google Chrome Extension
Another way to view cached pages and cached websites is to use Chrome extensions.
You can use the Web Cache Viewer Chrome extension.
Search for “Web Cache Viewer” extension on Google and add it to your browser:
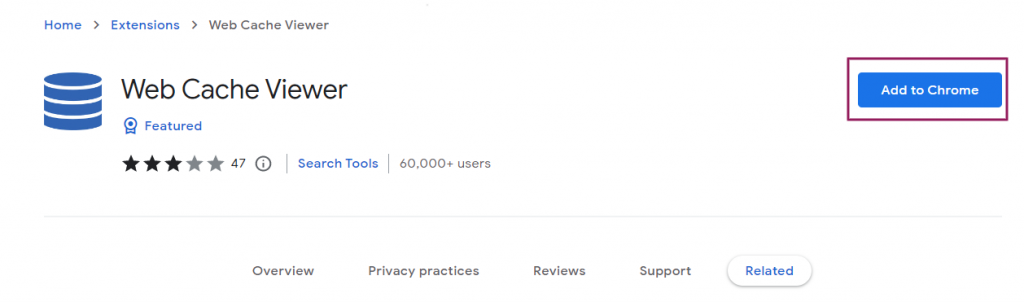
Image via Web Cache Viewer
Once installed, go to any web page on your site and click on any link, and point to “Web Cache Viewer:
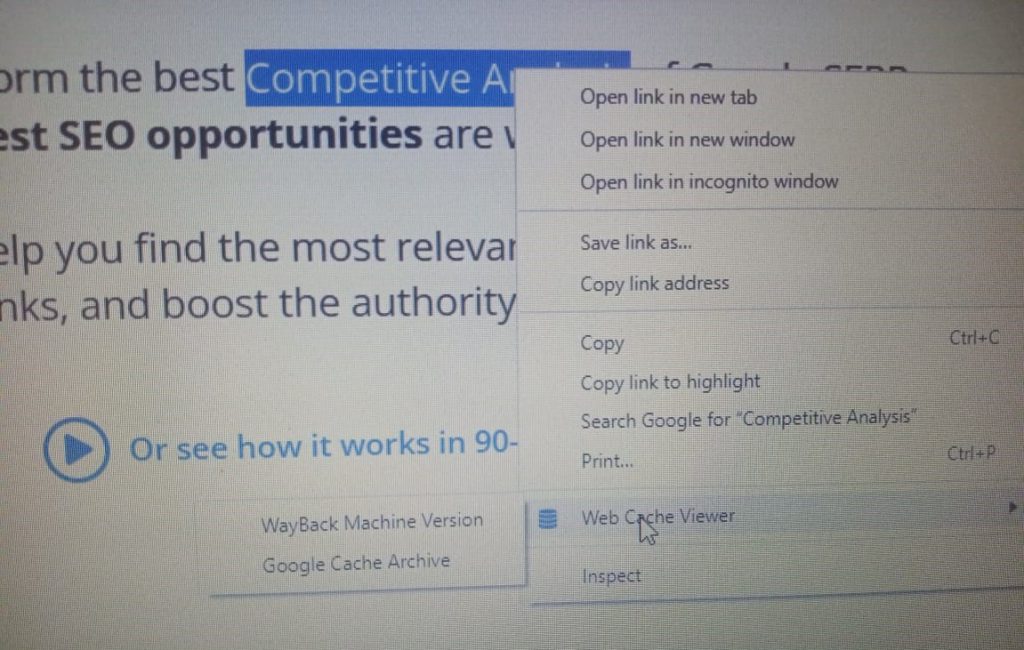
Image via SEO Buddy
From there, you can choose to view the Wayback Machine Version or Google Cache Archive of the cached page.
When you choose any of the options above, you will be taken to the Google cache version of the page.
3. Other Tools to Check Cached Websites
There are also other tools you can use to view cached copies of a web page.
The easiest one is the Wayback Machine. It is a powerful Google cache checker founded by the Internet Archive—a non-profit making organization located in San Francisco, California.
You can find billions of web pages saved on the World Wide Web saved as snapshots over time.
Follow the steps below to view cached sites/pages:
- Go to the Internet Archive site and enter the URL or keyword of the site/page you want to view the cached version of and click on “browse history”:
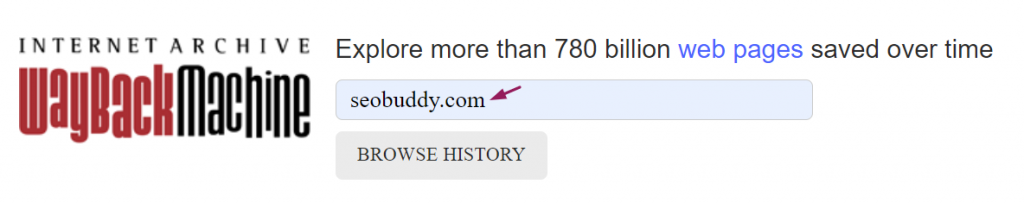
Image via Wayback Machine
- This will open a calendar interface where you can choose the cached version of a web page for specific dates:
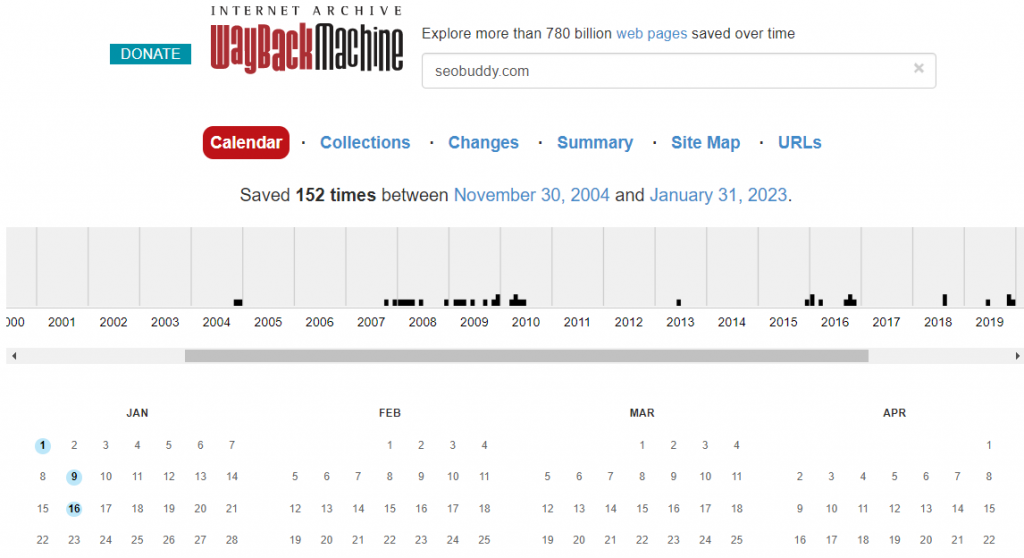
Image via Wayback Machine
You can use this tool on Google Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari to view the internet archive of web pages.
Note that the information displayed can be outdated, especially for older versions that were cached several years ago.
You can also use Google Cache Checker.
This is one of the free tools provided by Small SEO tools that can help you view up to 5 URLs.
Go to the tool and enter up to 5 URLs each on a separate line like this then click the “Check Google Cache” button:

Image via Google Cache Checker
This will take you to the page below:
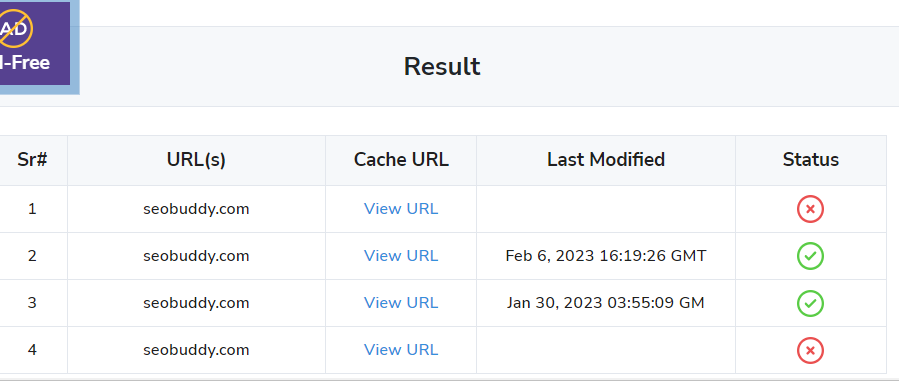
Image via Google Cache Checker
When you click on “View URL” in the “Cache URL” column, you will be taken to the cached version of your chosen page.
Note that, some pages will return a 404 error as shown below:
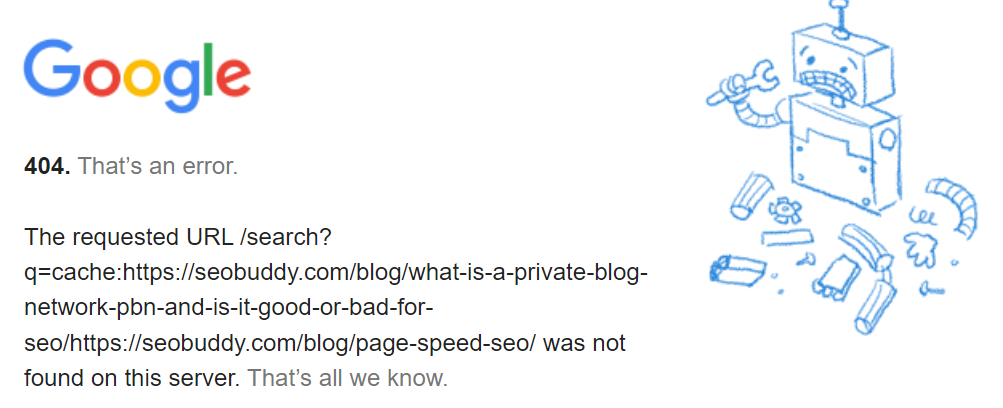
Image via Google
Read on to learn why you can’t find your cached page.

Now it’s time to discover the other 102 steps that will get more organic traffic flowing to your website. Get the SEO Checklist here.
Want to get a sneak peek of what it looks like?
Enter your email and get a free demo version of the SEO Checklist.
Reasons Why There is No Cached Version of a Page?
When you get a 404 error, it means the page has no cached version. Here are possible reasons why you might not find your cached web page.
Google Doesn’t Cache All Pages
Even though Google crawls an entire website, it might not cache all the pages on it. However, this isn’t something to worry about as it doesn’t imply that the page isn’t indexed and cannot be ranked on Google.
Here is a Twitter reply by Google’s search advocate, John Mueller, to a user who had asked why Google’s cached version of a page returns a 404 error:
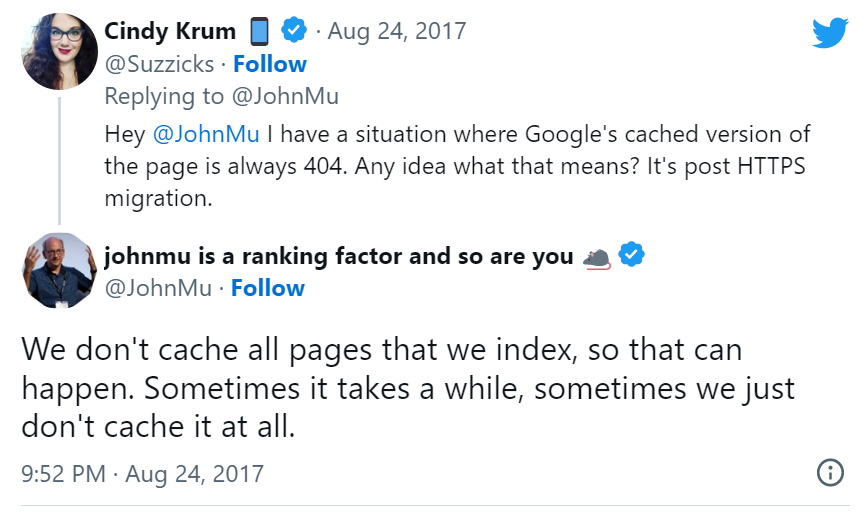
Image via Twitter
Your Page Isn’t JavaScript-Powered
Some JavaScript-powered pages are easier to index by Google than others. Of course, many JavaScript pages might not be cached or indexed.
This is especially true because most of the HTML is loaded after JavaScript executes.
Thus, if there are no pages to index, Google won’t cache the page.
A Meta Tag Might Prevent Caching
Two factors can prevent a page from being indexed and cached by Google.
First, if the page’s HTML code contains a noindex meta tag it won’t be indexed by Google.
Second, if there is a noarchive tag in the page’s HTML code, the page can’t be cached.
Either of the two tags will prevent Google from caching a page. To solve the problem, you may consider removing the noindex or noarchive tags.
Google Thinks That The Page is a Duplicate
Sometimes a page might not be cached when Google thinks it’s a duplicate. You may find ways to make the page unique by considering the search intent of the duplicate pages.
As you can see, you cannot rely on Google’s cache to determine whether Googlebots are crawling your site since not all pages crawled are cached.
A good rule of thumb is to check your website’s log files to view the last date and time Google crawled a page.
How to Fix Web Pages That are Not Cached
As mentioned above, having uncached pages isn’t something to worry about. However, if you want them to get cached by Google, here are a few things to do:
Submit Your Page to Google Search Console
Head over to Search Console and enter the page’s URL in the URL inspection search bar.
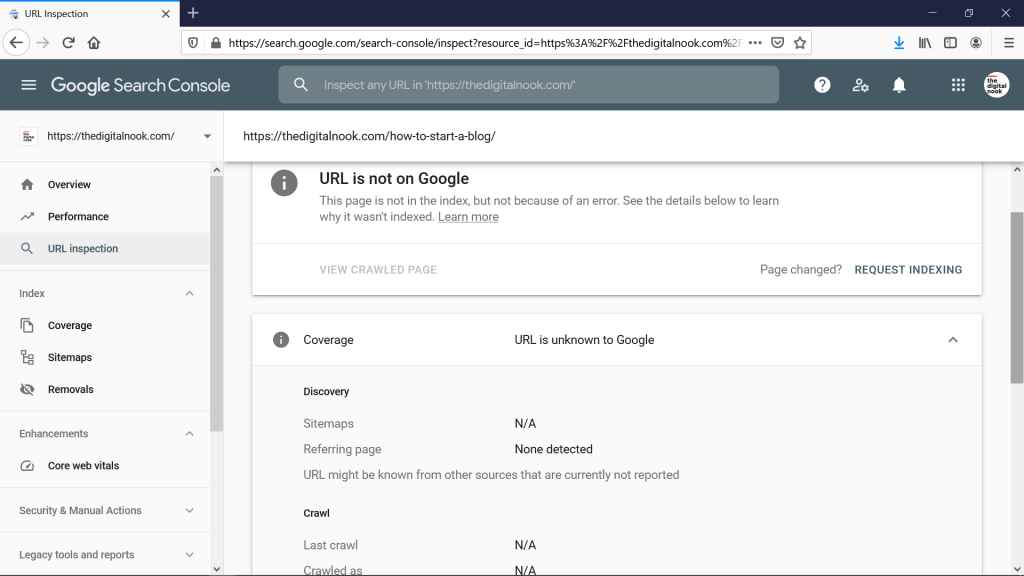
Image via Google
If you see “URL is not on Google”, it means the page isn’t indexed. If you recently made changes to the page and you think Google hasn’t indexed the current version, you can click Request Indexing to ask Google to re-index it.
Fix Any Technical Issues
The other method to fix problems with web pages that are not cached is to ensure your site is of high-quality and updated with fresh content regularly.
Additionally, ensure your site loads faster and is optimized for mobile devices.
Reasons Why You Should Conduct Google Cache Search Regularly
Performing a regular Google cache search is beneficial in many ways, such as:
Helps You to Check for Duplicate Pages/Content
Having duplicate pages or content on your site can hurt your SEO efforts.
Besides, when Google finds two similar pages, the search engine may decide to cache one and leave the other.
While there are other sophisticated ways to check duplicate content, using Google cache search is the simplest method.
It Helps You to Fix Technical Issues
Website technical difficulties are inevitable. Unfortunately, it’s not easy to determine when they might arise.
And when they occur, they might render your website unavailable.
Luckily, by viewing Google cache search results regularly, you can rest assured that users can interact with your site even when your site isn’t loading correctly.
Helps to Ensure Your Marketing Efforts Pay Off
After focusing all your efforts on creating high-quality content and optimizing it effectively, you want to ensure Google is crawling and indexing it.
A quick Google cache search can help you view cached pages and those that aren’t thus helping you to improve your website performance.
Spy on Your Competitors and Improve Accordingly
Every website owner desires to keep their website at the top of Google search results, above their competition.
But a slight change by your competitor on their website can outrank you without your knowledge.
Performing a frequent Google cache search on your website can help you track the changes they’ve made recently.
Can Help You Retrieve a Recent Version of Your Site
Tens of thousands of websites are hacked every day. Unfortunately, no one knows when hackers will strike.
Sadly, once hackers penetrate your site, you lose access to it and all the effort you have put into building it may go to waste.
Luckily, with Google cache search, you can retrieve a recent version of your website in the Google cache to rebuild your site.
What are the Limitations of Google Cache Search?
By investigating your website’s Google cache search results regularly, you gain helpful information that can help you improve your website performance greatly. However, there are some limitations you need to know.
It’s Not Easy to Tell When Your Page Was Last Crawled
While Google cache may show the date and time the last snapshot was taken, it’s not easy to tell when your pages were last crawled.
So where can you get accurate information?
Pro Tip: If you want to learn how often, why, and which bots Google crawls your website with, look at the data on Google Search Console.
Go to Settings in the sidebar on Search Console to find the crawl report.
Note that Search Console will only display information at the domain level so you can’t see how often Google crawls each page.
The Cached Page Might Not Be Rendered Properly
In the past, Google’s Web Rendering service—that’s responsible for rendering live pages—used to rely on an outdated version of Chrome.
Additionally, updated browsers sometimes rendered cached pages that are different from Google-rendered ones.
However, some progress has been made on Google rendering.
Currently, Google’s Web Rendering Service is based on the latest version of Google Chrome.
However, if you’re using an old version of Chrome, the cached page might not be rendered properly.
Another issue that leads to improper rendering is when the code that Google backs up refers to missing or modified resources. In that case, the page might be rendered incorrectly.
Google Might Display The Wrong Page
If Google detects duplicate content/pages or if it detects incorrect canonical tags, the cache might show the wrong page.
Google Doesn’t Cache All Your Website Pages
Another reason why you can’t completely rely on Google Cache Search for improving your website is that Google doesn’t always cache all your website pages.
This doesn’t mean that pages that aren’t cached aren’t important to Google or aren’t crawled.
How to Remove Cached Pages
No doubt Google Cache is important. However, you might not want your target audience to see an old version of your website/page stored on the cache.
For instance, as an ecommerce website owner, you might not want your customers to see certain product pages because you have discontinued the products on those pages.
To prevent Google from caching these product pages, you may consider including noindex and noarchive tags in the source code. This tells Google that you don’t want these pages to be indexed, archived, or cached.
You can also prevent Google from caching some content on your site by following the steps below:
- Go to Search Console and click “Removals” in the sidebar.
- Click on “New Request” then either choose “Clear Cached URL” or “Temporarily Remove URL”.
With temporary removal, the URL will not be displayed in Google search results for approximately six months. This means that it won’t be cached.
When you choose the clear cached URL option, the cache will be clear, but the page will be re-cached when Google crawls your site again.
FAQs
1. How do I find the cached version of a website?
To find the website’s cache, follow this simple process:
- Go to Google.com and type in the URL of the website or keyword then hit enter.
- Click the three dots menu on the search results then choose “Cached” on the tab that appears on the right-hand side.
- From there, you can view the full version, text-only version, or source code of the website.
You can also type “cache:URL” of the webpage without spacing on Google and hit enter.
2. How long does Google cache last?
Google backs up webpages in the cache for approximately 90 days or until Google bots crawl the page again,
3. What does a Google cached page look like?
Google cache page contains the URL of the page’s cache, the date the page was cached, and its different versions.
4. What Is Google cache?
Google cache is a backup of a page or content which is usually stored during Google crawls.
5. Why is Google cache important for SEO
Learning how to use Google cache search is a great idea for anyone interested in SEO to grow their organic traffic.
By viewing Google cache versions of your webpages and learning how to leverage Google cache properly, you can understand how Google crawlers interpret your content.
Conclusion
Google Cache search is a vital tool. Even though you might not use Google cache regularly, it can be helpful to check and diagnose any technical issues on your site.
When used together with Google Search Console, it can greatly help you to improve the performance of your website.
Do you want to get your website to page #1 on Google but aren’t sure how to do it?
Grab our SEO Checklist that will guide you on every important SEO step you need to take to optimize your website and generate more organic traffic.
Start driving a constant stream of customers to your website now.




